Administrator’s Guide
Secure Data Exchange (SDE) Server
Document Information
This document is for informational purposes only. Safe-T Data makes no warranties, express or implied, in this document. Safe-T is a registered trademark of Safe-T Data A.R Ltd. in the United States and other countries. The names of other companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
The information contained in this document, or any addendum or revision thereof is proprietary of Safe-T Data A.R Ltd. and is subject to all relevant copyright, patent and other laws and treaties protecting intellectual property, as well as any specific agreement protecting Safe-T Data A.R Ltd. rights in the aforesaid information. Any use of this document or the information contained herein for any purposes other than those for which it was disclosed is strictly forbidden.
Safe-T Data A.R Ltd. reserves the right, without prior notice or liability, to make changes in equipment design or specifications. All specifications are subject to change without prior notice. Safe-T Data A.R Ltd. assumes no responsibility for the use thereof nor for the rights of third parties, which may be affected in any way by the use thereof.
This document may contain flaws, omissions or typesetting errors; no warranty is granted nor liability assumed in relation thereto unless specifically undertaken in Safe-T Data A.R Ltd.’s sales contract or order confirmation. Information contained herein is periodically updated and changes will be incorporated into subsequent editions. If you have encountered an error please notify Safe-T Data A.R Ltd.
About This Guide
Version
This guide describes how to administer, configure, and customize Safe-T® Secure Data Exchange (SDE) Server 7.3.0.
Audience: System administrators with experience managing Microsoft servers, networks, and security.
How To Use This Guide
Safe-T recommends learning about the Safe-T SDE product as follows: 1: Read from this section How To Use This Guide to the top of External Tools. This will provide you a high-level understanding of Safe-T SDE.
2: Read the sections Safe-T Administration Console: Day-To-Day Tasks to the bottom of Connect to the Organization’s SMTP Server.
3: Read these sections: Manage Safe-T SDE Licenses, Reference Section, Troubleshooting and the Glossary.
4: Become familiar with the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in User Guide.
Many of the policy parameters you learn to configure in this Admin guide are relevant for the three end user interfaces: Safe-T Outlook Plug-in, Safe-T web portal, and mobile app for iOS and Android.
Safe-T SDE Administration Interfaces
Safe-T SDE administrators use these interfaces: • Safe-T SDE Administration Console: The web-based Safe-T SDE Administration Console provides day-to-day administrative access to the main features, settings, and status information related to the Safe-T SDE server.
• Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool: The Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool is a Windows-based application used for initialization tasks you do not perform frequently. For more information on the tasks you can perform with each administration interface, see Safe-T SDE Admin Interfaces: Tasks.
Main Subjects In This Guide
This table lists the main subjects in this guide and concisely describes each subject.
Related Documentation
For more information on Safe-T SDE see the following:
• Safe-T SDE Installation Guide
• Safe-T SDE Upgrade Guide
• Safe-T Outlook Plug-in User Guide
• Safe-T Outlook Plug-in Installation Guide
• LNK-Connector Administrator’s Guide
• Safe-T Secure Data Access Administrator’s Guide
What is Safe-T SDE?
Safe-T SDE enables organizations to securely exchange data of any type and size between people, applications, and businesses. Safe-T SDE is built on the industry’s widest range of pre-configured application connectors and is powered by an automated security policy enforcement engine.
Safe-T SDE offers multiple innovative solutions to securely grant access and transfer shared data. All solutions provide key “where, what, who, and when” tracking data for each transferred file. These solutions are ideal for B2B and C2B transactions.
Safe-T SDE implements a unique modular architecture with integration capabilities that ensure it seamlessly integrates into legacy data platforms in the enterprise.
For an illustration of a standard, typical Safe-T SDE server deployment, see, Standard Deployment.
Secure Data Exchange
• Broker, control, and secure data exchange of any type and size between people, applications, cloud solutions, and businesses.
• Protect both inbound and outbound data exchange including email, S/FTP, consumer cloud access, file uploads, mobile data exchange, and employee collaboration (EFSS).
• Add security and access control across a wide variety of enterprise data exchange patterns.
• Control and secure file sharing and upload solutions including authentication, data scanning, and file encryption.
• Deploy a highly secure and authenticated end-to-end solution for financial transactions: Digital check deposits, ATM withdrawals, wire transfers, and email requests.
• Reduce the chance of ransomware attacks by controlling your stored files: Integrity: encryption, true-type, file size, and by ensuring all file manipulation is done as authorized.
Integrated Data Security Platform
Unified Protocol
• Native and SDK based support for all common enterprise file transfer and business application protocols.
• Integrate new RFC protocols or modify existing ones.
• Real-time application/protocol conversion (HTTP to SFTP, SQL to DropBox). Authentication Gateway
• Built-in multi-factor authentication and authorization (MFA) engine.
• Integrate Safe-T SDE with any number of authentication and authorization systems. SecureStream™ policy and workflow engine
• Broker traffic to 3rd party security (DLP, AV, anti-malware) and IAM products.
• Automatically enforce security policies on outgoing/incoming data exchange flows.
• Create multi-factor authentication, authorization, and other data exchange workflows. Connectors
• Approximately 50 compiled connectors are available for integration with enterprise applications, data storage, cloud storage/solutions, security services, authentication, encryption, and more.
Secure Virtual Vaults (SVV) technology
This is completely optional and not required for this tutorial!
Safe-T SDE Security Policy Enforcement
Safe-T SDE enforces security measures using both 1) policies and 2) external tools.
• Policies: Configurable sets of parameters that are primarily responsible for defining security restrictions on end users. For more information, see Safe-T Object Relationships and How To Create Policies.
• External tools: Security applications that operate on files in a Safe Space. Each Safe-T SDE server can run a configurable sequence, or a complex workflow of built-in and third-party tools that implement services. For more information, see External Tools.
Examples of services that can be provided by external tools: File encryption, antivirus (AV), data leak prevention (DLP), copying files to a remote server in a different network segment, connecting to another Safe-T SDE server, and other services.
Safe-T SDE server ships with approximately 50 compiled connectors enabling organizations to easily implement and run many third-party security applications on files stored in Safe-T SDE Safe Spaces.
Note: Although Safe-T SDE supplies connectors to integrate with many leading security applications (e.g. encryption, antivirus, DLP), Safe-T SDE does not supply the .exe files or licenses for proprietary third-party products.
Overview Safe-T SDE Objects
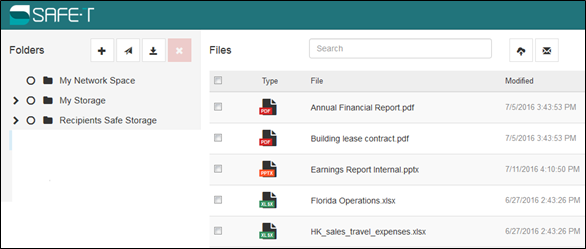
Safe Spaces
Safe-T SDE digital vaults, or folders, are called Safe Spaces. A Safe Space contains data from a source that often is transparent to users. A Safe Space can reside on the Safe-T SDE server, a network file storage location, FTP/SFTP site, or in an MS SQL database.
Tip: Safe-T SDE allows, but does not require, Safe Space folders to be stored within its local storage.
You can connect Safe Spaces to one or multiple groups. Users then access Safe Spaces based on the user’s group membership. You also can grant access to a Safe Space by connecting a Safe Space directly to a specific user.
Using the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in, Safe-T web portal, and mobile app, users upload/download files and send files by email selecting various levels of transport security.
Important: The file upload/download functionality is like other file sync and share solutions. However, Safe-T stores uploaded files in Safe Spaces where policies and external tools enforce strict, customized security.
When a Safe-T Outlook Plug-in user sends an email with file attachments the files are uploaded to a special Outlook Safe Space. The Outlook Safe Space is not visible or accessible to users. The Safe Space is used as a storage area for intended email attachments.
Recipients are delivered the sent email message in their email client. However, recipients download file attachments securely from the Safe-T web portal after authentication instead of receiving file attachments via a non-secure email path.
Safe-spaces are configured to work either in Storage or Archive mode. For descriptions of these two modes, see How To Create Safe Spaces.
Policies
Safe-T SDE supports approximately 100 configurable policy parameters that enable and enforce data security. Most policy parameters are geared to enforcing secure operations by end users.
A policy is a Safe-T object that can be connected to one or more groups. A Safe-T SDE administrator creates group policies and procedures for secure data sharing and exchange that can be integrated into existing business work flows. See: Safe-T Object Relationships.
Notes:
- Policies enforce security at the user level (e.g. file access expiry, download limits), and external tools enforce security by performing operations on files (e.g. file encryption, virus scanning, DLP, copy files to another server).
- Policies are connected to groups.
Info: You can optionally connect a policy to a Safe Space. Doing so will override the group’s policy only for that specific Safe Space. For more information, see How To Create Policies.
Groups
A group is a collection of users who share a single Safe-T SDE policy and have permission to access specified Safe Spaces. See: Safe-T Object Relationships.
You can create groups/policies/Safe Spaces in any convenient order.
However, when you are getting started you may want to create objects in this sequence: Groups, Users, Policies, and Safe Spaces.
Info: You can connect a group to one policy and to multiple Safe Spaces.
You can create groups based on any logical approach that is useful to your organization’s business requirements.
For example, you can align Safe-T groups as follows:
• Departments (marketing)
• Roles (system administrator)
• Level in the corporate chart (managers)
• Geographic location (Tampa Bay office)
Example: Create a Safe-T SDE Sales group and a Sales Managers group. You can connect both groups to one policy, but you can grant the Sales Managers group access to additional Safe Spaces.
Default Groups
Safe-T SDE supplies default groups. The purpose of these groups is to get you started with some examples of groups.
Note: You can use these four default groups, modify them, or delete them.
• Organizers: Connected to Standard policy and the Organizer work mode.
• Publishers: Connected to Standard policy and the Publisher work mode.
• Recipients: Connected to Safe Reply policy and the Organizer work mode.
• System: Connected to Administrator policy and the Organizer work mode.
Info: You can create a group, or multiple groups, and configure them with a Publisher mode attribute. A group configured as “Publishers” grants to users in that group limited access to Safe-T SDE features. Publishers have permission only to send secure emails and they have no access to Safe Spaces.
To learn more about Publisher groups, see Group Publisher Mode.
Import LDAP Groups If you want, you can import your organization’s LDAP groups into existing Safe-T SDE groups. The group properties, LDAP tab, displays a link to add LDAP groups.
You can import multiple LDAP groups into a single Safe-T SDE group.
Note: You must create a Safe-T SDE group before you can import LDAP groups. An LDAP user who is a member of multiple LDAP groups can belong to only one Safe-T SDE group. For more information, see How To Import LDAP Groups.
Users
A Safe-T SDE user account enables a person or application to log in and use these services:
• Safe-T web portal: Upload/download files to Safe-T SDE Safe Spaces and send secure emails with links to stored files. Users can select many sending options.
• Safe-T Outlook Plug-in: Upload/download files to Safe-T SDE Safe Spaces and send secure emails with links to stored files. Users can select many sending options.
• Safe-T mobile app: Upload/download files to Safe-T SDE Safe Spaces and send secure emails with links to stored files. Users can select many sending options.
• As an email recipient: Registered users can download file attachments (secure content) by authenticating with their Safe-T SDE user name and password. Users who are not registered, can be authenticated using an email or SMS OTP (One time password) verification code.
For more information, see How To Create Users.
Safe-T Object Relationships
There is no mandatory order you need to follow when creating and connecting Safe-T objects. You can create Safe-T object relationships in a flexible manner.
Note: An exception is you must create the policy you want to connect to a group before you create the group.
One strategy to start building your enterprise logic into the Safe-T SDE server is to create your organization’s required policies and groups then connect to each group a single policy.
For more information on creating policies and groups, see How To Create Policies and How To Create Groups.
Next, populate the groups with users. You can create new users one at a time manually or import your organization’s existing LDAP groups.
For more information on creating users, see Create New Users, and Group Properties > Import LDAP Groups.
Create Safe Spaces and connect each Safe Space to one or more groups. For more information on creating Safe Spaces, see How To Create Safe Spaces. In a Safe Space, you can assign groups and end users various permissions to perform operations on Safe Space files.
Tip: There is no limit on the number of users, groups, policies, and Safe Spaces your organization can create.
Figure 1: Safe-T SDE Object Relationships

Figure 1 shows an organization that has implemented four groups and three policies. The diagram illustrates these rules:
• A user can be a member of only one group. If you import users from Active Directory, those users can each be a member of only one Safe-T SDE group because a Safe-T SDE user cannot be connected to multiple (i.e. potentially conflicting) policies.
• A group can be connected to only one policy. Each group is connected to a policy that can enable, enforce, and define values for approximately 100 different policy parameters. For more information, see Reference: Policy Parameters.
• A group can be granted access to multiple Safe Spaces.
• A policy can be assigned to multiple groups.
Users are connected by way of their group membership to files that reside in Safe Spaces. However, in the user’s details window, an administrator can optionally Add, Edit, or Delete for that user the Safe Spaces that specific user can access.
Info Example policies: These are snippets of policies corresponding to the Figure 1 diagram.
The policies illustrate higher security restrictions applying to members of the Accounting and Finance Department group than to members of the Technical Account Managers, and Software Developers groups.
Finance Department Policy
• Enforce Message Encryption = Yes
• Enforce OTP = Yes
• File Expiration Date = 3 days
• Enable Max Downloads = Yes
• Max Downloads = 2
Technology Managers Policy
• Enforce Message Encryption = Yes
• Enforce OTP = Yes
• File Expiration Date = 7 days
• Enable Max Downloads = Yes
• Max Downloads = 4
Software Developers Policy
• Enforce Message Encryption = No
• Enable OTP = Yes
• File Expiration Date = 15 days
• Enable Max Downloads = Yes
• Max Downloads = 10
About Permissions
This section is concerned with administrative permissions on Safe-T SDE objects. Administrative permissions can be granted to groups and users to create, modify, remove, and view Safe-T SDE objects.
Objects Managed With The Safe-T SDE Administration Console
• Safe-Spaces
• Policies
• Groups
• Users
• Role Management
• License Management
• File Types Management
• System Reports
Each of the objects listed above contains an Edit Permissions button on its main web page you open from the navigation pane.
Objects Managed With The Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool
• External Tools
• Database Configuration
• System Configuration
• Encryption Management
• Disk Quota Management
Note: The objects listed above do not have their own Edit Permissions web page. For the objects listed above, use the Edit Permissions page for Roles to connect groups and users to the objects.
Full details on how to manage roles and permissions are described here: How To Create And Apply Roles.
Safe-T SDE Server Interfaces
Safe-T SDE administrators use these interfaces:
• Safe-T SDE Administration Console
• Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool
The administration interfaces were described in the section Safe-T SDE Administration Clients.
The Windows Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool is used for initialization and other infrequent tasks an administrator does not need to perform day-to-day. The web-based Safe-T Administration Console is used for day-to-day tasks.
Caution: If there is a duplicate command or task you can perform using either administrative interface, use the command or perform the task using the web-based Safe-T SDE Administration Console.
Safe-T SDE Administration Console
The web-based Safe-T SDE Administration Console provides day-to-day administrative access to the main features, settings, and status information related to the Safe-T SDE server. For more information, see Safe-T Configuration Tool: Initialization Tasks.
Info: In Safe-T SDE version 7.3.0, an administrator, or a user with any other role, must be an Active Directory user to log into the Safe-T SDE Administration console and to be granted any permissions on Safe-T objects (e.g. Groups, Safe Spaces, Policies).
Tip: One exception to the above rule: Local administrators can log into the Safe-T Administration Console and has full permissions on all Safe-T objects.
Prerequisite
Important: You must use the Safe-T SDE Windows admin interface to edit the web.config file as explained here: Extension #25: Management Service.
To log into the Safe-T SDE Administration console:
- In a web browser, enter either of these URLs:
• https://
• https://
Tip: You should access the Safe-T SDE Administration console using the host name value configured in the SSL certificate’s Common Name (CN) field. Doing this enables you to validate an SSL connection to the host.
- Enter the username and password for your system account. When you log into the admin console, “Overview” window appears. The admin console sections are labeled in the figure below.
Figure 2: Administration Console

Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool
The Windows Safe-T Configuration Tool is for administration tasks you do not need to perform day-to-day. For more information, see Safe-T Administration Console: Day-To-Day Tasks.
Examples of Safe-T Configuration Tool tasks:
• Manage encryption keys.
• Configure Safe-T SDE server connection attributes.
• Use a wizard to create and configure an IIS Safe-T web console used as the end user web portal for file upload/download and data sharing.
• Configure external tools.
For more information on the allocation of tasks for each administrator server interface, see Safe-T SDE Admin Clients: Tasks List.
Info: The web-based Safe-T SDE Administration console is used to perform day-to-day Safe-T SDE administration tasks.
Safe-T SDE End User Clients
Safe-T SDE supports three end user interfaces:
• Safe-T Outlook Plug-in
• Safe-T web portal
• Safe-T mobile app for iOS and Android
All Safe-T SDE interfaces provide users upload/download access to digital vaults and enable users to send secure emails.
Info: End users can use the Safe-T web portal to send emails with various levels of transport security, upload/download files, and file-sharing. The Safe-T web portal does not require your organization to use Microsoft Outlook.
Tip: For more information about the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in, see the Reference section Safe-T SDE Clients in this guide and review the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in User Guide.
Safe-T Outlook Plug-in
The Safe-T Outlook Plug-in adds a Secure Transport tab and related buttons to the standard Outlook ribbon.
In Outlook, users can access their Safe Spaces in two ways:
• Click the SmarTransfer button.
• Click the SmarTransfer [Safe-T SDE] link in the Outlook navigation pane.
Figure 4: Outlook Email Plug-in
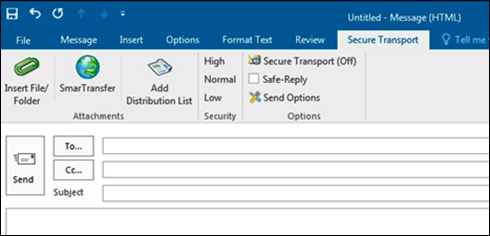
Figure 5: Outlook Plug-in: Safe Space files.

Safe-T Web Portal
Users registered in Safe-T SDE and ad hoc email recipients who are not registered interact with Safe-T SDE using the organization’s Safe-T SDE IIS website.
• Each registered user defined in Safe-T SDE can access a web page to manage secure file uploads/downloads and send secure web-based emails.
• Email recipients, registered and ad hoc, can access encrypted email messages and file attachments using the IIS website.
To log into the Safe-T SDE Web Portal:
- In a web browser, enter either one of these URLs:
• https://
• https://
Tip: End users should access the Safe-T SDE web portal console using the host name value configured in the SSL certificate’s Common Name (CN) field which enables you to validate an SSL connection to the host.
The following image shows the default Safe-T web portal login page:
Figure 6: Login Web Page

Safe-T Web Portal
Users registered in Safe-T SDE and ad hoc email recipients who are not registered interact with Safe-T SDE using the organization’s Safe-T SDE IIS website.
• Each registered user defined in Safe-T SDE can access a web page to manage secure file uploads/downloads and send secure web-based emails.
• Email recipients, registered and ad hoc, can access encrypted email messages and file attachments using the IIS website.
To log into the Safe-T SDE Web Portal:
- In a web browser, enter either one of these URLs:
• https://
• https://
Tip: End users should access the Safe-T SDE web portal console using the host name value configured in the SSL certificate’s Common Name (CN) field which enables you to validate an SSL connection to the host.
The following image shows the default Safe-T web portal login page:
Figure 6: Login Web Page

For information about customizing the appearance of the Safe-T SDE IIS website, see How To Customize the Safe-T IIS Website.
- Enter your user name and password.
- Click Submit. The Safe-T web portal home page appears.
Figure 7: Safe-T Web Portal
Safe-T Configuration Tool: Initialization Tasks
Use the Windows Safe-T Configuration Tool to perform initialization and other configuration tasks you need to perform infrequently.
Info: This table describes the tasks each administrative interface can perform: Safe-T SDE Admin Clients: Tasks List.
You access most initialization tasks on the Safe-T Configuration Tool > Tools menu including the tasks described in these sections:
• Tools Menu
• External Tools
Apply External Tools To A Safe Space
Info: Use either the Safe-T SDE Windows or web admin console to apply external tools to a Safe Space.
Adding and configuring extensions (Tools > External Tools) prepares external tools for use. After you configure external tools, you must connect them to Safe Spaces. The external tools operate on newly added files uploaded to a Safe Space.
Note: External tools can also operate on files uploaded to any arbitrary folder using the Folder Monitor extension. The monitored folder does not have to be a Safe Space. For more information, see How To Monitor Any Folder.
To connect external tools to a Safe Space:
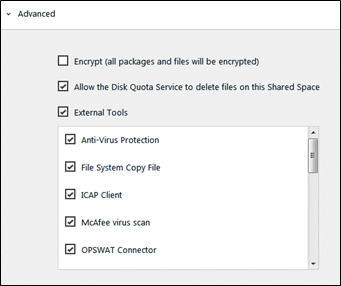
- Open a Safe Space and in the Advanced Settings section select the external tools you want to run.
- Save the configuration.
Info: The Safe Space > Advanced Setting section is populated by the applications you configured in the main File System Event Role external tools window.
Figure 8: Safe Space Advanced Settings
Apply An External Tools Template To A Safe Space
An external tools template is a default configuration of external tools. All new Safe Spaces you create will be configured with the default selection of external tools you define in the template.
Info: You can use the Safe-T SDE Web or Windows admin console to access this feature.
To create an external tools template:
- In the Safe Space creation/edit wizard Advanced Settings section select the external tools you want to configure as a template and apply to the current Safe Space.
Figure 9: Web UI Example: Create External Tools Template
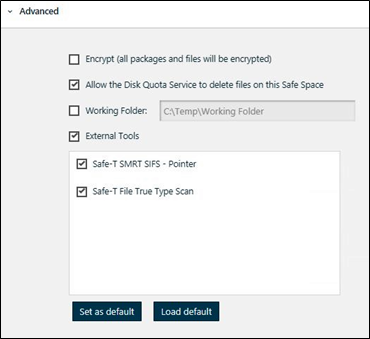
Figure 10: Windows Example: Create External Tools Template

- Select ‘Set As Default’ and click Save.
Info: If you change a Safe Space’s selected external tools, or if you edit an existing Safe Space, you can reload the set of external tools defined in the template by clicking ‘Load Default’.
To load the external tools template:
- Open the Safe Space creation/edit wizard Advanced Settings section.
- Click ‘Load Default’.
Safe-T Administration Console: Day-To-Day Tasks
Use the web-based Administrator console for frequent tasks you perform day-to-day. These tasks include:
• How To Create Groups
• How To Create Users
• How To Create Safe Spaces
• How To Create Policies
• How To Create Roles
Tip: For more information on the tasks you can perform using the Safe-T Administration console, see Safe-T SDE Admin Clients: Tasks List.
What Are Safe-T SDE Users
You create Safe-T SDE users manually and/or import LDAP groups and users into Safe-T groups. See, How To Create Users and Create New Users.
Each Safe-T user is connected to a group and is assigned the group’s policy which controls many aspects of how the user interacts with the system. For more information, see Policies.
A Safe-T SDE user can log in and use these interfaces:
• Safe-T web portal.
• Outlook Plug-in (If your organization uses Microsoft Outlook and has licensed the Safe-T SDE Outlook plug-in).
The Safe-T web portal and Outlook Plug-in provide users access to Safe Spaces and contain files accessible by that specific user.
For more information, see Safe-T SDE End User Clients and Safe Spaces.
Users access their Safe Spaces by logging into the Safe-T web portal or by selecting the SmarTransfer [Safe-T SDE] link in the Outlook plug-in navigation panel.
Working with Safe Spaces, users upload/download files and send file attachments by email and select various levels of email message and file transport security.
Tip: The file upload/download functionality is like other file upload applications. However, Safe-T SDE stores uploaded files in Safe Spaces where policies and external tools enforce strict security conditions.
As email recipients, Safe-T SDE users download encrypted secure emails and file attachments using by default their Safe-T SDE or Active Directory user name and password instead of an OTP verification code.
Email recipients who are not registered as Safe-T SDE users, for example business customers, can access encrypted emails and file attachments by authenticating using an OTP verification code.
An administrator can configure the Safe-T SDE server to send the ad hoc, non-registered email recipients an OTP by a separate email or SMS message.
How To Create New Users
In the Administration Console, creating users is integrated with creating and editing groups.
Info: You cannot create a stand-alone user that is not a member of a group.
For more information, see these sections:
• How to create a user manually: Create New Users.
• How to import existing LDAP groups: How To Import LDAP Groups.
How To Use Advanced Search
How To Find Users
Use the Safe-T SDE Windows Admin Console to access this feature.
The Find Users feature enables you to locate records of users in Safe-T SDE. If you enter a search string (e.g. “james”) your search will find users James.Smith and James.Roberts.
To find users:
- In the Safe-T SDE main window, click the Find menu. The Find Users window appears.
Figure 11: Find Users Window

- Enter these details:
• Find: Enter a search string (e.g. Emily) that is the target of your search.
• Search by: Select a search operator: Like, Equal, Starts with, Ends with.
• Active users only: Set the search engine to look only for active users or all users.
Info: In a user’s properties window there is a checkbox for enable/disable user.
- Click Search. The search results appear and displays this information:
• User name: Displays the full user name.
• Email: Displays the email of the user.
If you select a user record in the results window, the user’s properties window appears.
[Use the Safe-T SDE Web Admin Console to access this feature.]
The Advanced Search feature enables you to locate records of users in Safe-T SDE.
You can also view the user’s properties and which Groups and Safe Spaces are connected to the user.
To find users:
- In the Safe-T SDE web admin navigation pane, click Groups. The Groups web page appears. In the upper right corner locate the Advanced Search button.
- Click Advanced Search. The Advanced Search box appears.
- Enter a search string and click Find. In this example we search for ‘admin’.
The Search results lists all users with ‘admin’ in their user name.
Example: Search for ‘admin’.

If you want to view the user’s properties, click the Name link. In this example, click ‘Admin’.
- If you want to view the user’s membership in a Group and access to Safe Spaces, click the arrow on the left side of the name.

How To Find Safe Spaces
The Advanced Search feature allows to you to search for Safe Spaces in Safe-T SDE. You can also view the Safe Space properties and the users who have access to the Safe Space.
To find Safe Spaces:
- In the Safe-T SDE web admin navigation pane, click Safe Spaces. The Safe Spaces web page appears. In the upper right corner locate the Advanced Search button.
- Click Advanced Search. The Advanced Search box appears.
- Enter a search string and click Find. The Search results lists all Safe Spaces with ‘my’ in the Safe Space name.
Example: Search for ‘my’.
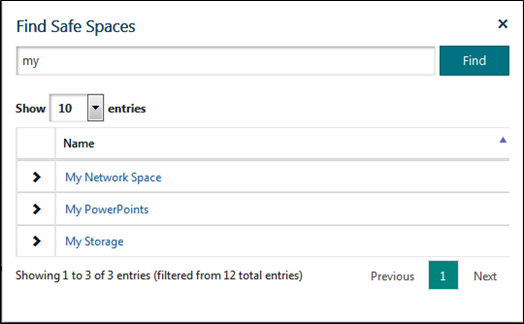 If you want to view the Safe Space’s properties, click the Name. In this example, click ‘MyPowerPoints’.
If you want to view the Safe Space’s properties, click the Name. In this example, click ‘MyPowerPoints’.
- If you want to view the Safe Space’s connections to users, click the arrow on the left side of the name.
Example: Users with access to the Safe Space: MyPowerPoints.

How To Find Policies
The Advanced Search feature enables you to search for Policies in Safe-T SDE.
You can also view the Policy properties and the Groups and Safe Spaces that are connected to the Policy.
To find Policies:
- In the Safe-T SDE web admin navigation pane, click Policies. The Policies web page appears. In the upper right corner locate the Advanced Search button.

- Click Advanced Search. The Advanced Search box appears.
- Enter a search string and click Find. The Search results lists all Policies with ‘st’ in the Policy’s name.
Example: Search for ‘st’.

If you want to view the Policy’s properties, click the Name. In this example, click ‘Standard’.
- If you want to view the Policy’s connections to Groups and Safe Spaces, click the arrow on the left side of the name.

How To Create Groups
Create groups that correspond to your enterprise’s business logic.
For example, groups can reflect your corporate chart, regional office locations, partners, contractors, customer email safe-reply recipients, etc.
A group is a collection of users who share a single policy and who have a set of permissions to access one or multiple Safe Spaces.
Tip: You cannot create a new group and assign to it a policy that is not yet defined. Before you start to create a group, be sure you create the policy you want to assign to the group.
Create A New Group
This section describes how to create a new group by defining the minimum number of parameters: group name and assigned policy.
To create a Safe-T SDE group:
- In the Admin console navigation pane, select Groups. The Groups web page appears.
Figure 22: Groups Web Page

- Click New Group.
Figure 23: Create New Group
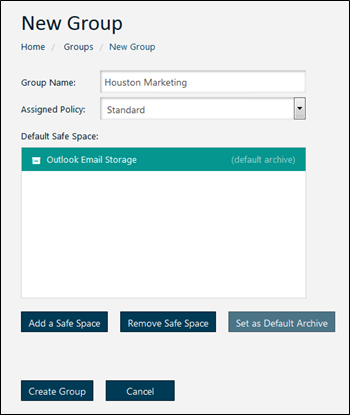
Enter values for these fields:
• Group Name: The name of the group.
• Assigned Policy: The policy you want to assign to the group.
- Click Add a safe Space. A pop-up window appears.
Figure 24: Create New Group

- Select the Safe Space archive that is used for storing Outlook file attachments. Click OK.
- Select the Safe Space archive you chose in step #4 then click Set as Default Archive.
[You have now completed the minimum configuration to create the group.]
- Click Create Group. The new group appears listed. By default, the group name column is sorted alphabetically.
- Click the group name or pencil icon to open the group properties web page.
Tip: The new group you created does not yet contain any users. You must add users to the new group and configure several additional group properties.
Figure 25: Group Properties

Create New Users
You can create new users one at a time manually using the New User button in a group’s properties page.
Info: The most efficient way to add users to a Safe-T SDE group is to import users in bulk from existing company LDAP groups. See, How To Import LDAP Groups.
To create a new user manually: In a Group properties web page click New User.
Figure 26: Create New User

A wizard appears that enables you to configure parameters for the new user.
Figure 27: New User: General Information

Enter values for these fields:
• User Name: Enter a user name. The user name cannot contain a space. • Password: Enter a password. The password must contain at least 6 characters and is case-sensitive.
• Auto-Generate: Automatically generates a password for the user. The password is displayed to the Safe-T SDE administrator as asterisks.
Note: If you select Auto-Generate password, you must also enable Send Utilities in the group properties web page to enable Safe-T SDE server to send login credentials to the user. For more information, see Group Properties > Send Utilities.
• Password expiration date: Set an optional expiration duration for the user’s password. You configure the expiration duration by setting a time span in minutes/hours/days/months.
• Allow password change: If the checkbox is selected, when the password expires the user is sent an email with a new password. If this checkbox is cleared, when the password expires the user is locked out of Safe-T SDE.
• Inactive User: If this checkbox is selected, the user cannot access any Safe-T SDE services.
• Assign license: Assign a license from the license pool to the selected user.
• Remove license: Remove the license from the selected user. Click Next.
Figure 28: New User: Details
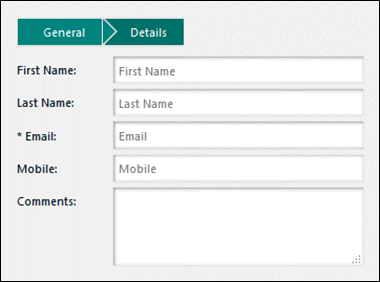
Enter values for these fields:
• First name, last name: Enter the user’s first and last name.
• Email, and mobile: Enter the user’s email address and mobile phone number.
• Comments: You can save notes about this user.
Click Save. The new user is created.
Info: Additional user parameters are available by editing the user’s properties.
Edit Users
When you edit a user’s properties, you can modify more parameters than you can configure when you create a new user.
For example: By editing a user’s properties you can assign to the user a certain type of Safe Space that is accessible to multiple users who transparently use a common encryption key.
The same task cannot be performed when creating the new user.
For more information, see How To Manage Encryption Keys For Shared Safe Spaces.
To edit a user’s properties:
- In the Group properties web page click the name of the user or the pencil icon at the right side of the user’s row.
Figure 29: Edit User: General Information

- Enter values for these fields:
• User Name: Enter a user name. The user name cannot contain a space.
• Password: Enter a password. The password must contain at least 6 characters and is case-sensitive.
• Auto-Generate: Automatically generates a password for the user. The password is displayed to the Safe-T SDE admin as asterisks.
Note: If you select Auto-Generate password, you must also enable Send Utilities in the group properties web page to enable Safe-T SDE to send login credentials to the user.
• Password expiry date: Set an optional expiration duration for the user’s password. You configure the expiration duration by setting a time span in minutes/hours/days/months.
• Allow password change: If the checkbox is selected, when the password expires the user is sent an email with a new password. If this checkbox is cleared, when the password expires the user is locked out of Safe-T SDE.
• Inactive User: If this checkbox is selected, the user cannot access any Safe-T SDE services.
• License key: Displays if the user has a valid license assigned. If there is no assigned license, the time remaining for the Demo license is displayed.
• Send user’s instructions: Displays a Send Utility window, enabling you to configure the Safe-T SDE server to send login credentials and links to installation files.
• Assign license: Assign a license from the license pool to the selected user.
• Remove license: Remove license from the selected user.
- Click the Details section.
Figure 30: Edit User: Details

- Enter values for these fields:
• First name, last name: Enter the user’s first and last name.
• Email, and mobile: Enter the user’s email address and mobile phone number.
• Comments: You can save notes about this user.
• Reset User Quota: You can set the user’s quota to the initial amount of disk space allowed.
- Click the History section.
Figure 31: Edit User: Report

A report appears showing the history of recent email send events for the user.
- Click the Safe Spaces section.
Figure 32: Edit User: Safe Spaces

Info: The main method for users to connect to a Safe Space is to inherit access permissions from users’ enclosing group.
However, in user details there are two methods to connect a user to a Safe Space. These direct methods do not involve the user inheriting access from the group:
• Use the Choose button to connect a user to an existing Safe Space. If the Safe Space is encrypted, users with access to the Safe Space can access only their own files.
• Use the Add button to create a new Safe Space you configure to be encrypted (i.e. Safe Space > Advanced > Encrypt checkbox) and connect it to the user. This method creates an encrypted Safe Space that uses a common key. Users connected to the Safe Space can access all encrypted files in the Safe Space.
For more information about encrypted Safe Spaces, see How To Manage Encryption Keys For Shared Safe Spaces and Safe Space > Advanced Settings.
Tip: The Safe Space you use to store your company’s Outlook emails should always use unique, per-user, encryption keys and the Outlook Safe Space should not be visible. You do not want a user to be able to access other users’ emails.
Select one of the following: • Choose: A popup window with available Safe Spaces appears. Select one and click Save.
A user connected to an encrypted Safe Space accesses their files only with their own unique key.
• Add: Create a new encrypted Shared Space that uses a common encryption key and click Save.
• Edit: Select a Safe Space, edit it, and click Save.
• Delete: Select a Safe Space, delete it, and click Save.
The parameters on the right side of Edit User > Safe Spaces are read-only. When you sect a Safe Space from the list these details appear:
• Safe Space path: Path of the Safe Space.
• Safe Space Type: Local Safe-T SDE server drive, Network location, FTP site, SFTP site, or MSSQL database.
• Visible (Show UF on web browser): Is the Safe Space visible by end users. The Outlook Safe Space should not be visible to end users.
• Set this UF to be the package folder: This checkbox is selected if selected if the Safe Space is Archive type.
Configure Group Properties
This section describes additional group properties.
Group Properties Security Distribution Group
In the Group > Select a group > Group properties button > click Security & Distribution Group.
Figure 33: Group Properties > Security & Distribution Group

In the Security & Distribution Group section you can do the following:
• Import LDAP groups.
• Configure email distribution groups.
For detailed information on importing LDAP groups, see How To Import LDAP Groups.
Info: A security group marked “True” indicates the group is a part of the parent group. The users in a security group are listed in the Group Properties web page.
A security group marked “False” indicates the group is a not part of the parent group but has a permissions relationship with the parent group for email exchange via distribution lists.
• Add LDAP Group(s): Imports existing LDAP groups. The imported LDAP group members become, after their first Safe-T user login, a member of the Safe-T parent group.
• Add Safe-T Group(s): Import existing Safe-T groups for email distribution lists.
• Global Permissions: Users in the group can send Safe-T emails using a distribution list file that contains email addresses of any recipient whether they are in a Safe-T group or if they are ad hoc users.
When users in the group compose an email, and enter a recipient’s email address in the “To:” field, address autocomplete will operate if the recipient is in any group listed in the LDAP tab window.
• Explicit Permissions: Users in the group can send Safe-T emails using a distribution list file that contains email addresses of recipients but only if the recipients are members of pre-configured mapped groups.
When users in the group compose an email and enter a recipient’s email address in the “To:” field, address autocomplete will operate if the recipient is a member of pre-configured mapped groups.
For more information about email distribution lists, see Group Properties > Distribution tab.
Group Properties Safe Spaces
Safe-T SDE digital vaults, or folders, are called Safe Spaces. A Safe Space contains data from a source that often is transparent to users.
Info: In the Unified Folders section, you can connect the group you are configuring to one or multiple Safe Spaces. See, Overview: Safe-T SDE Objects. The users in a group inherit the connections to the Safe Spaces.
To add Safe Spaces to the group:
- Click Add Safe Space. A list appears of the Safe Spaces the group is already connected to.
Figure 34: Group Connected To Safe Spaces

- Click Add a Safe Space. A pop-up window appears.
Figure 35: Add a Safe Space

- Select the Safe Space you want to connect to the group and click OK.
Note: Repeat steps #1 and #2 if you want to connect the group to multiple Safe Spaces.
Info: The “default archive” is the Safe Space used to store an organization’s Outlook Emails. Each user can access only their own files.
To set a Safe Space as the default archive:
- In the list of Safe Spaces connected to the group, select the Safe Space you want to use as the Outlook folder.
- Click Set as Default Archive.
To remove a Safe Space connection to the group:
- Select the Safe Space then click Remove Safe Space. The Safe Space connection is removed, but the Safe Space itself is not deleted.
Group Properties Safe Reply
Safe-T SDE enables users to send Safe Reply email invitations to registered or ad hoc email recipients. The Safe Reply recipients can reply to the sender with an email message and file attachments using Safe-T SDE secure channel, security scanning, and audit trail features.
In the Safe Reply section, select the Safe Space you want to use to implement the Safe Reply feature.
Figure 36: Choose A Safe Space For Safe-Reply

• Use this group: Select from the list a Shared Space that is connected to the group you are configuring. The Safe Space you select will be used to implement the Safe Reply feature.
• Select a group: Select from the list a different group. Your Safe Reply Safe Space is determined by the other group’s Safe Reply Safe Space.
Group Properties Advanced
To enter the group advanced settings, in the Security & Distribution Group web page click the properties icon on the right side of a group. A pop-up web page appears displaying the Security tab.
Group Properties Security tab
Figure 37: Security Tab

A security group marked “True” indicates the group is a part of the parent group. The users in a security group are listed in the Group Properties web page.
A security group checkbox that is cleared indicates the group is a not part of the parent group but can have a permissions relationship with the parent group for email exchange via distribution lists.
For more information, see Group Properties > Security & Distribution Group.
Group Properties Delivery tab
The Delivery tab allows you to set delivery restrictions by mapping a whitelist and blacklist.
Figure 38: Delivery Tab

• White list: the white list defines a list of the only email recipients permitted to receive messages.
• Black list: the black list defines a list of recipients who are not allowed to receive messages.
Info: Filtering email addresses by white list and black list is often considered mutually exclusive.
The purpose of the message restrictions window is to provide you both filtering strategies. You can enable/disable the filtering option best suited for your organization.
Group Properties Distribution tab
Figure 39: Distribution Tab
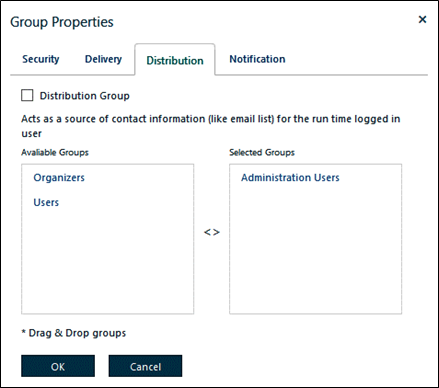
Tip: The Safe-T Outlook Plug-in supports sending emails in bulk using a CSV file containing email addresses. The Distribution tab is relevant only if inter-group permissions = Explicit. Also, this feature works in the Outlook-plugin only when Secure Transport is On.
For more information about inter-group permissions, see Group Properties > Security & Distribution Group.
The Distribution tab enables members of the group you are configuring to send emails using a distribution list file but only when the email addresses are included in an explicit list of recipient groups you configure in this tab.
The distribution list file list contains email addresses. You can comma delimit them (CSV) or place one email address on each line pressing Enter to terminate each line.
The groups configured in the Distribution tab are only potential bulk email recipients. There is no requirement that in your distribution list file you must include potential email recipients. The sender of a bulk email distribution is not required to include all recipient groups or users mapped in the Distribution tab.
Example: How you can configure the group Organizers to have subgroups whose members can be email recipients of a bulk mailing by an Organizer user who has created an email distribution list file.
To add bulk email recipient groups to the group Organizers:
- Import to the Organizers group existing Safe-T SDE and/or LDAP groups you want to add as potential email recipients. You can import groups from the properties web page > Security & Distribution Group section.
[Now you must select the Distribution List checkbox for each of the subgroups you imported.]
- In the Organizers group > Group Properties> Security & Distribution Group section, click the properties icon on the right side of one of the groups.
Figure 40: Security & Distribution Tab
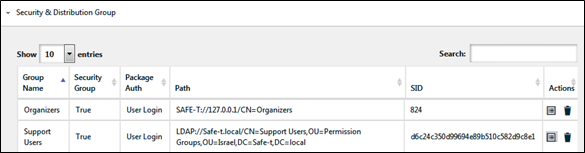
A pop-up web page appears.
- Select the Distribution tab then Select the Distribution Group checkbox.
Figure 41: Distribution Group Checkbox

- Click OK.
- Repeat the above steps to select the Distribution Group checkbox for each subgroup you imported that you want to include as potential bulk email recipients.
- Open the policy assigned to the group in the Edit Policy web page. Select the checkbox: “Restrict access to distribution group”.
Figure 42: Restrict Access To Distribution Group

In the same policy, you have to enable displaying to end-users the Add Distribution List button. Select the Enable Add Distribution list parameter:
Figure 43: Enable Add Distribution List
In the Outlook Plug-in, if you select Secure Transport you will see in the Outlook ribbon a button labeled: Add Distribution List.
Figure 44: The Add Distribution List In The Outlook Plug-in
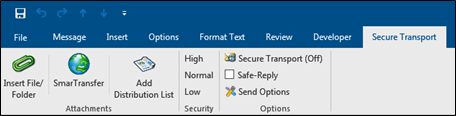
When a user selects Add Distribution List, a browse window opens enabling the user to select the distribution list text file.
Group Properties Notifications Tab
Figure 44: Group Message Notification

The Notification feature allows you to send email alerts to a recipients list. The alerts are sent every time a user uploads a file to the related Safe Space.
• Group Message Notifications: Set if the option is active.
• Add Related Group: Add the related group(s) for notification alerts.
Group Properties Send Utilities
More detailed admin manual of this method is available Here
Groups > Send Utilities enables an administrator to send end users credentials, installation files for the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in, and other client utilities.
An administrator can send utilities to either:
• An entire group
• An individual user
To send utilities to all members of the group:
- In the Groups web page click: Send Utilities. The Utilities section appears.
Figure 46: Send Utilities

Available Items an administrator can send
• Link to the web interface and send user’s credentials
• Outlook Plug-in installation file
• Console Utility
Distribution Method:
• Send a file to administrator
• Distribute via email
• UAC Compliant
Tip: You can perform unattended client deployments using the Windows System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and Group Policy Object (GPO) capabilities. For more information, see the Outlook Plug-in Installation Guide.
- In the Groups web page click Send Utilities > Select the Message section.
Figure 47: Send Utilities > Message
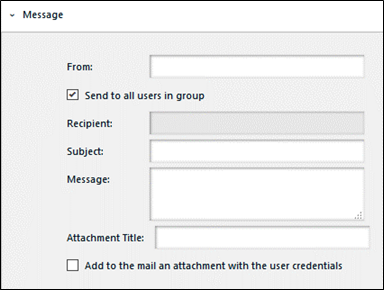
• From: Enter the name or ID of the sender.
• Send to all users in group: Send in bulk to all members of the group.
• Recipient: Enter the comma separated email addresses of the utilities recipients.
• Subject: Enter a Subject of the message.
• Message: Enter a message.
• Attachment Title: Enter a descriptive package name.
• Add to the email an attachment with the user credentials: Add file attachments.
- In the Groups web page click: Send Utilities > Select the Security section.
Figure 48: Send Utilities > Security

• Invitation Expires After: If the sent item is a link, set a duration after which the secure invitation expires.
• Secure Invitation with (OTP) One Time Password: Require recipient authentication using an OTP.
• Limit amount of downloads per user to # downloads: Set the maximum number of file attachments downloads.
The next two parameters are relevant only if the Administrator is sending to login credentials.
• Password expiry (in days): Set a duration after which the end users passwords expires.
• Allow password change: Allow or prohibit end users changing the sent password.
- In the Groups web page click: Send Utilities > Select the Policies section.
Sending utilities to a user is like sending utilities to an entire group.
To send utilities to a single user:
- Open a user’s details for editing, for example: Group > Organizers > user’s details.
- Click the link: Send Users Instructions.
Figure 49: Send Users Instructions

A web page appears that is the same as previously described for sending utilities to an entire group. Enter values in the Utilities, Message, Security, and Policies sections the way you configured sending utilities to a group.
Group Properties Publisher Mode
This section describes how to create one Publisher group, or multiple Publisher groups.
**All groups have a Working Mode attribute that can have one of two values: **“Organizer” or “Publisher”. Organizer is the default value and refers to a standard group.
A user in a publisher group can log into the Safe-T web portal and send emails with file attachments uploaded from the user’s local PC or network, but not from Safe Spaces.
Info: Users in a publishers group do not have access to Safe Space folders or files.
To designate a group as publishers:
Info: You configure the Working Mode attribute using the Windows Safe-T Configuration Tool.
- In the navigation pane, click the group you want to configure.
- In the group properties window, click the link displaying the group name, then in Group properties select Working Mode: Publisher.
Group Working Mode Publisher
Figure 50: Set Group Working Mode: Publisher or Organizer

A user in a publisher group can access the Safe-T end user web portal for sending secure emails.
Figure 51: Email Client For Users In Publisher Group

Group Properties Import LDAP Groups
You can import Active Directory (AD) groups into existing Safe-T SDE groups.
Info: Importing LDAP groups is a quick and easy way to create Safe-T SDE user accounts for members of your AD groups.
About Imported LDAP Users
Imported LDAP users have characteristics of both Safe-T users and LDAP users.
• Imported LDAP users continue to have their user credentials managed in Active Directory.
• As Safe-T SDE users, they will be able to log into Safe-T SDE interfaces (Outlook Plug-in and Safe-T web portal) using (by default) their Active Directory user name and password.
• The imported LDAP users will have Safe-T SDE group properties, an assigned policy, and permissions to access files in Safe Spaces.
Note: An LDAP user who is a member of multiple LDAP groups can belong to only one Safe-T SDE group.
Also see: What Are Safe-T SDE Users.
Group Properties Permissions
In Safe-T SDE you can grant to an LDAP user or group permissions on all of a certain type of Safe-T object. For example, permissions to add, modify, remove, or view all Safe-Spaces, policies, groups, users, roles, external tools, etc. For more information, see How To Create And Apply Roles.
This section describes how you can grant permissions on specific groups.
Note: Safe Spaces, policies, and groups are the only Safe-T objects that support granting permissions on specific Safe-T objects.
To learn how to grant permissions on a specific group, see the steps described here: How To Grant Permissions on Specific Safe Spaces, Policies, and Groups.
How To Create Safe Spaces
Safe-T SDE digital vaults, or folders, are called Safe Spaces. The contents of a Safe Space are usually stored in an encrypted format. An administrator can grant groups and users permissions to access one or multiple Safe Spaces.
Each Safe Space contains data from a source usually transparent to users.
Typically, users are granted view and upload/download permissions to more than one Safe Space. From an end user’s perspective, they have access to folders and files.
A Safe Space can reside on the Safe-T SDE server, a network file storage location, FTP/SFTP server, or in an MSSQL database.
If you select to encrypt the contents of a Safe Space, encryption/decryption is done automatically on file upload/download.
About Shared Access
Info: If the Safe Space is not encrypted, all users connected to that Safe Space can access all packages and files.
There are two ways to configure shared access to an encrypted Safe Space:
• Unique keys: Users who have permission to access the Safe Space can view and upload/download only their own files in the Safe Space.
• Shared keys: Users who have permission to access the encrypted Safe Space can view and upload/download any of the files in the Safe Space.
For more information, see How To Manage Encryption Keys For Shared Safe Spaces.
About Folder Mode
There are two ways to configure the mode of a Safe Space: either Storage or Archive.
• Storage: Windows Explorer type of folder. This is the standard storage mode for a Safe Space.
• Archive: This type of Safe Space is intended to store data such as Safe-T Outlook Plug-in file attachments for an entire organization. For more information, see Safe Space > General.
Info: Start with a new empty folder when you create an encrypted Safe Space. Encryption operates on file upload/download.
If you have existing unencrypted files in a folder you want to use as an encrypted Safe Space, the following occurs: The unencrypted files already residing in the folder will be “decrypted” by the system on download. This will corrupt the files because the files were not encrypted.
How To Display All Safe Spaces
You can display a list of all Safe Spaces connected to your Safe-T SDE server. To display a full list of Safe Spaces associated with your Safe-T SDE server:
- In the navigation pane, select Safe Spaces.
Figure 52: Safe Spaces List
The Safe Spaces web page displays the following information: • Name: The name of the Safe Space.
• Type: The type of the selected Safe Space. For example: Local Safe-T SDE server drive, Network location, FTP site, SFTP site, or MSSQL database.
• Path: The path to the Safe Space.
• Safe Space folder type: The file storage mode: Storage or Archive.
For information about Safe Space folder types, see Safe Space > General Tab.
To create a new Safe Space:
- In the navigation pane, click Safe Spaces. A table of Safe Spaces appears.
- Click New Safe Space.
Figure 53: Create New Safe Space
A wizard starts that helps you create the new Safe Space.
Safe Space General
Figure 54: New Safe Space > General

- Enter a display name and description of the Safe Space. For example, (Name) Seattle_Marketing, (Description) Contains files for the Seattle, Washington marketing unit.
Important: The name you specify is a display name or an alias. End users view and interact with the display name of the Safe Space. The actual name of the Safe Space folder is part of the path you specify in the Connection wizard page and is unknown to the end users.
Tip: You should always use a Safe Space display name, or alias, that is different from the actual Safe Space folder name. This makes it more difficult for a malicious user to hack into any Safe Space.
- Select either Storage or Archive folder types.
• Storage: Windows Explorer type of folder. This is the standard mode.
• Archive: This type of Safe Space is intended to store data such as Outlook Plug-in file attachments.
Unlike a flat, simple folder, an Archive folder type creates a tree directory adding a unique new leaf-level folder identified by a GUID for each file stored. Example: C:\SafeSpace\Outlook\Archive%User%\MyStorage\2016\10\09
Figure 55: Example of Archive Type Safe Space
Tip: An Archive folder eliminates file-naming conflicts for organizations that use a single Outlook Safe Space to store all user file attachments. The tree structure also speeds processing time.
• Visible: Specify if you want the Safe Space to be visible to users. The Outlook file attachments folder should not be visible to users.
- Click the Connection section.
Safe Space Connection
This wizard page enables you to configure connection parameters between the Safe Space you are creating and the Safe-T SDE server.
Figure 56: New Safe Space > Connection

Enter the following details: • Type: Select Local Safe-T SDE server drive, Network location, FTP site, SFTP site, MSSQL database, or another Safe-T SDE server.
• Path: Enter the path to the Safe Space. The right-most component of the path is the actual name of the Safe Space folder. The path you specify including the Safe Space folder name must be unique.
Info: If you include the %UserName% placeholder in the path, the system will create a subfolder for each authorizer user when that user attempts to access the Safe Space for the first time.
• Enable Credentials: Select the checkbox and enter the server name, user, and password.
Note: The credentials fields (Server/Login/Password) are not enabled if you select Safe Space Type = Local.
• Use secure connections only: Enforces a secure connection between the Safe-T SDE server and your Safe Space.
• Certificates: Opens a “browse for” window enabling you to manage client-side certificates.
• Proxy: You can use your organization’s proxy server if you configure and enable it.
- Click Next.
Safe Space Security
The security tab enables you to do the following: • Grant groups and users access and permissions to the Safe Space.
• Configure a policy that is connected to the Safe Space.
Note: Usually, policies are connected to groups. However, you can configure a policy for a Safe Space that overrides the existing group policies. The policy defined for a Safe Space is limited and effective only for interactions with the specific Safe Space you are creating.
Tip: If you change the Default Group Policy, that configured policy overrides group policies but only for this Safe Space.
To grant groups and users access and permissions to a Safe Space:
- In the Security section, specify which groups and/or users can access the Safe Space. Click in the “Select a User or Group” box to display a list of users and groups.
Figure 57: New Safe Space > Security
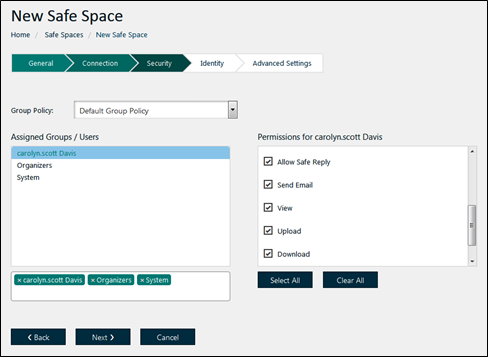
- Set access permissions. Permissions are applied to users and groups individually. For example, you can assign different permissions to the Organizers and Publishers groups.
The available permissions are: • Allow safe-reply
• Create folder
• Delete file
• Delete folder
• Download
• Download sub tree
• Send email
• Share
• Upload
• View
- Click Next.
Safe Space Identity

• Enhanced Security Mode: Provides extra security for API based access and not for user based access. In this mode, only a connection that specifies the UFID explicitly will be permitted to access the Safe Space.
If you select the checkbox, users cannot access this Safe Space via these Safe-T SDE modules: Outlook Plug-in, Safe-T Web portal, Mobile.
• UFID: Sets the UFID identifier of the selected Safe Space. The value can be any alphanumeric characters with a maximum length of 255 characters.
Note: Unified Folder ID (UFID) uniquely identifies a Safe Space.
Click Next.
Safe Space Advanced Settings
In the Advanced Settings tab, you can enable Safe Space encryption, the disk quota clean-up service, and you can activate your configured external tools.
How To Encrypt Files Uploaded To A Safe Space
You can encrypt files uploaded to the Safe Space using either of these two methods:
Figure 59: New Safe Space > Advanced Settings

• Select the Encrypt checkbox: Uploaded files are encrypted using AES-256 encryption at the client side. The client can be the Safe-T Outlook plugin or a web browser. Because the files are encrypted by the client, you cannot use this option if you want to run external tools such as DLP that require files to be scanned as clear text.
• Select the Encrypt checkbox and configure the File Encryption AES-256 external tool: Uploaded files are encrypted using AES-256 encryption at the server side and the AES-256 Encryption external tool runs in the workflow according to its sequential position.
The above two encryption options are the only valid configurations. Specifically, if you choose to run the encryption at the server side using AES-256 encryption external tool you must also select the checkbox: Encrypt.
Note: You should configure the AES-256 encryption external tool to run at, or near the end of the external tools workflow. If for example you want to run DLP scanning, you must first run the DLP scan on the clear text files before you encrypt the files in the Safe Space.
Info: When you create a new encrypted Safe Space use an empty folder. Encryption operates on file upload and decryption on file download. Any unencrypted files already residing in the Safe space folder will be “decrypted” by the system on download. This will corrupt the files because the files were not encrypted.
• Allow the disk quota service to delete files on this unified folder: Allows the disk quota process to delete files from the selected folder. For information on configuring the disk quota clean-up process, see Manage Disk Quota.
• Working Folder: Eliminates possible file use concurrency issues by isolating the process of running a sequence of external tools on one or more files. Enabled by default. For more information on the Working Folder feature, see Safe Space Working Folder.
• File system event role: Allows you to set which external tools run on files you upload to the Safe Space. For details on external tools, see External Tools.
Click Finish.
Info: When you create a Safe Space, you can immediately see a record in the Admin console of the new Safe Space along with the path you set.
Important: The Safe Space folder is not yet created in the actual Safe Space server path.
You need to perform two additional steps: • Connect the Safe Space to a group.
• Use the Safe-T web portal or Outlook Plug-in to upload one or more files to the Safe Space.
When you complete these two additional steps, the Safe Space is created in the path you set.
Verify file encryption and decryption If you selected the Encrypt checkbox, using a Safe-T client upload some files to the Safe Space. You can then navigate to the Safe Space path location to verify the files are encrypted.
After you verify the files are encrypted, download the encrypted files and verify the downloaded files have been automatically decrypted.
How To Manage Encryption Keys For Shared Safe Spaces
Info: This section is applicable only to encrypted Safe Spaces. If the Safe Space is not encrypted, any user with a connection to the Safe Space can access all of the contained files.
You can implement key management using any of these options:
Encrypt/decrypt files with each user’s unique key: Users who have permission to access the Safe Space can view and upload/download only their own files in the Safe Space. Safe-T SDE encrypts/decrypts files for each user with the user’s unique key.
Note: You implement unique individual access to a Safe Space using either of these techniques:
• Users inherit Safe Space connections from their group.
• Users are directly connected in user details, using the Choose button, to an existing Safe Space that was not created to use a common encryption key.
To encrypt/decrypt files in a Safe Space with each user’s unique key:
Method #1
- Navigation pane > Safe Spaces > New Safe Space > Advanced > Encrypt the Safe Space.
- Navigation pane > Groups > Specific Group > Safe Space > Choose the encrypted Safe Space.
Click Save. Users inherit Safe Space connections from their group.
Info: Users in the group can view and access only their own encrypted files in that Safe Space.
Method #2
- Navigation pane > Safe Spaces > New Safe Space > Advanced > Encrypt the Safe Space.
- Navigation pane > Groups > Specific Group > Open user record.
- In user record > Safe Space > Choose button.
- Connect the user with the Encrypted Safe Space.
- Click Save. The user accesses the Safe Space with the user’s unique key.
Info: The users can view and access only their own encrypted files in that Safe Space.
Encrypt/decrypt files with a common key: Users who have permission to access the encrypted Safe Space can view and upload/download any of the encrypted files in the Safe Space.
Safe-T SDE encrypts/decrypts all uploaded/downloaded files using one user’s key which is a common key used transparently by all users directly connected to the Safe Space.
To encrypt/decrypt all files in an encrypted Safe Space using a common key:
- Choose a Safe-T SDE user (e.g. Andrew) whose encryption key will be used by Safe-T SDE to encrypt/decrypt all files in a specific Safe Space.
- In the navigation pane, click Groups.
- In Groups, click the Group that contains the user (e.g. Andrew) you chose in step #1.
- Click the user’s name to open the record for editing.
- Click the Safe Spaces section then click Add.
- Create a new Safe Space.
- In Advanced Settings, select the Encrypt checkbox.
Example:

- Connect the user to the new encrypted Safe Space, then click Save.
Info: Andrew’s key will be the common key used by Safe-T SDE to encrypt/decrypt all files in the new Safe Space. Safe-T SDE’s use of Andrew’s user’s key is transparent to Andrew and to all other Safe-T SDE users.
Note: Unique key and common key Safe Spaces display different icons.
• Unique key Safe Space:
• Common key Safe Space:
- Grant additional users access to the common key Safe Space. In their User details > Safe Space section connect them directly to the shared Safe Space.
Tip: All file uploads/downloads to the Safe Space will be encrypted/decrypted using Andrew’s common key. From the users’ perspective, they have common access to encrypted files in a Safe Space.
How To Grant Permissions On Specific Safe Spaces
In Safe-T SDE you can grant to an LDAP user or group permissions on all of a certain type of Safe-T object. For example, permissions to add, modify, remove, or view all Safe-Spaces, policies, groups, users, roles, external tools, etc. For more information, see How To Create And Apply Roles.
To learn how to grant permissions on a specific Safe Space, see the steps described here: How To Grant Permissions on Specific Safe Spaces, Policies, and Groups
Note: Safe Spaces, policies, and groups are the only Safe-T objects that enable you to grant permissions on specific Safe-T objects.
How To Enable File Type Filtering {#how-to-enable-file-Type-filtering}
This section describes how to manage the global table of file types.
File type filtering enables you to control the file types members of a group are allowed or prohibited to upload to a Safe Space. You connect a file type filter to a group by defining the filter in a policy. Using file type filters is optional. You start to create a file type filter using a preconfigured default global database of file types you can customize.
Enabling file type filtering for a policy requires two steps:
- Navigation pane > Settings > Configure a global set of available file type definitions as described in this section.
- Navigation pane > Policy > Policy wizard > File Types. For each Safe-T SDE policy, create a table of file types that are allowed or prohibited. The file types must be selected from the global policies. See, New Policy > File Types.
To configure the global file types table:
- In the navigation pane, select Settings.
- Click File Types. The global file type table appears.
Figure 61: Global File Types
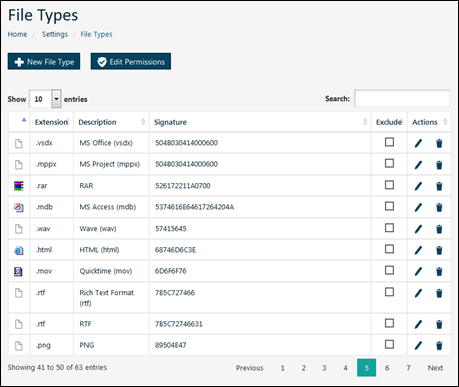
• Icon: The icon of the file.
• Extension: The file extension.
• Description: A description of the file type.
• Signature: The binary signature of the file used by Safe-T SDE to check the file type.
• Exclude: If selected, the file type is excluded from the binary signature test.
To edit global file types:
- In the global table of file types, select the pencil icon of the file type you want to edit. A pop-up screen appears similar to this:
Figure 62: Edit a File Type
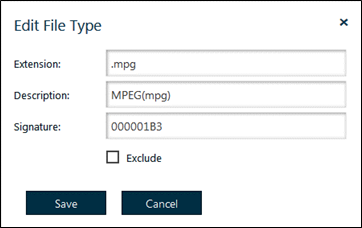
- Edit the file type parameters then click Save.
• Extension: The file extension.
• Description: A description of the file type.
• Signature: The binary signature of the file used by Safe-T SDE to check the file type.
• Exclude: If selected, the file type is excluded from the binary signature test.
To add a new global file type:
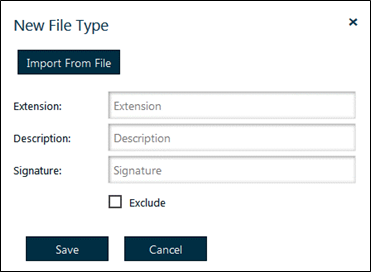
- In the File Types web page, click New File Type. A pop-up screen appears:
Figure 63: New File Type
- Configure the new file type parameters then click Save.
• Import From File: Enables you to fill in the parameters for a file type by browsing to a file. When you browse to a file, the Extension, Description and Signature values are filled in automatically.
Info: A value for the Exclude field is not automatically entered.
Example: Browse in your Windows Explorer to a Zip file. The new file types parameters are generated automatically.
Figure 64: New File Type
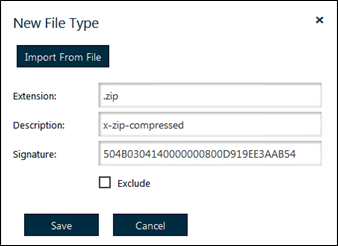
• Extension: The file extension.
• Description: A description of the file type.
• Signature: The binary signature of the file used by Safe-T SDE to check the file type.
• Exclude: If selected, the file type is excluded from the binary signature test.
You have now configured the global file types table.
How To Create An Outlook Archive Safe Space
This section describes how to configure a Safe Space that stores Outlook Plug-in file attachments. This Safe Space will store all email file attachments users send with the Safe-T Outlook Plug-in and Secure Transport: On.
The files stored in the Outlook archive will be restricted by file-related policy parameters such as: File expiration, max file size, and max downloads.
Also, according to how you configure the Outlook Safe Space, the files will be scanned with AV, DLP, and other external tools and will be subject to how you configure user disk quotas and file cleanup rules.
To create an Outlook archive Safe Space:
Step #1: Create Safe-Space
- Create a Safe Space you want to use as the Outlook archive. Users connected to this Safe Space access and encrypt email file attachments they send with their unique keys.
- When you create the Safe Space, configure it with the attributes: File Archive mode, and not visible.
- Name the Safe Space “Outlook”, “Outlook Archive”, or if you want to obfuscate the name choose any other folder name. “Outlook” is the default value.
Step #2: Connect Groups
Do the following for each group you want to use the Outlook Safe Space:
- Open the Group properties > Safe Spaces section.
- Select the Outlook Safe Space.
- Click Set as Default Archive.
Step #3: Connect With UFID
Use the remote UFID value to connect the Outlook Plug-in interface to the Safe-T SDE Outlook Safe Space.
- Open the Outlook Safe Space > Identity section.
The value of the Remote UFID set in the Safe-T SDE server (Safe Space > Identity > RFID) is required to match the value in the Outlook plug-in > Add-ins > Safe-T Settings > Connection tab > Remote UFID field.
Do not select Enhanced Security Mode. See, Safe Space > Identity.
- Edit the RFID either in the Safe Spaces > Identity section or in the Outlook Plug-in interfaces. Be sure the values in the Safe-T server and Outlook Plug-in interfaces are the same.
How To Create Policies
In this section, you learn how to configure a policy. A policy is a named set of policy parameters.
Safe-T SDE supports more than 100 configurable policy parameters that enable and enforce security features. Your organization can create as many policies as are required.
Policies are primarily responsible for defining security restrictions on end users. In contrast, external tools are security applications that operate on files uploaded/downloaded from a Safe Space. See, External Tools. Note: Each group can be connected to a single policy. A policy can be connected to many groups.
In some situations, you may want to connect a policy to a single user. You can do this by creating a group containing a single user or binding a specific Safe Space to a policy and connecting that Safe Space to a user: See, Safe-T Object Relationships and Safe Space > Security.
Policy parameter examples:
• Emails must always use a High or Normal security level.
• Safe replies from email recipients are allowed.
• Attachments can be downloaded a limited number of times.
• Attachments cannot be accessed after a certain number of days.
• Emails with attachments more than 2MB must be sent securely.
Note: Many of the configurable policy parameters relate to the Outlook Plug-in and Safe-T web portal features. It is recommended that before you create a policy, you should read through the Outlook Plug-in User Guide. Also, familiarize yourself with the table of Policy Parameters in the reference chapter.
Related Documentation
• Safe-T SDE Policy Parameters
• Outlook Plug-in User Guide
Create A New Policy
Safe-T SDE supports many configurable policy parameters that enable and enforce security features.
Some Safe-T SDE policy parameters are designated as enabling a security feature, and other parameters are designated as enforcing a feature.
In Safe-T SDE policies, the behaviors of parameters follow this rule:
• Enable: Sets a default value for a parameter a user can modify.
• Enforce: Sets a default value that a user cannot modify.
Important: When you create a policy, you can configure which file types to allow or exclude from Safe Spaces. Each policy you create that you want to add a file type filter requires you to select from the global table of file types the relevant file types for the policy. For more information, see How To Enable File Type Filtering.
To create a new policy:
- In the navigation pane, select Policies. A table of policies appears.
Figure 65: Policies Web Page
The Policies web page displays information on existing policies:
• Policy Name: The name of the policy.
• Description: A concise description of the policy.
• Enabled: You can enable/disable a policy.
• Default Policy: The policy that will by default be assigned to a group.
• Max file size: The maximum total size of email attachments a user can send.
- Click New Policy. A wizard appears that enables you to configure parameters for the new user.
New Policy General
Figure 66: New Policy > General
- Configure these parameters: General section
• Policy is: Select on or off to activate/deactivate the policy.
• Policy Name: Enter a name for the policy.
• Description: Enter a description of the policy.
• Policy expiration date: You can set an expiration date for the policy.
• Description: Disk Quota section
Note: You configure the disk quota management process using the Safe-T SDE Configuration tool. See, Manage Disk Quota. The configuration settings in a policy allow you to customize disk quota management for a specific policy.
• User Disk Space Quota: Set a maximum user disk quota.
• Disk Quota Clean-up (Archive): Select one of the following:
o Clean-up files after: Enter number of days.
o Clean-up file when package expires: File expiration is an optional policy parameter an admin can configure.
o Clean-up Method: Select either Permanently Delete, or Do Nothing (Reset Quota).
• User can delete files in shared-activity state (before they expire): When end users share Safe Space files using the Outlook Plug-in or Safe-T web console SmarTranfer, they send links to the files residing in a Safe Space. This is unlike sending email attachments. Sharing a file using a link creates a shared state. You can allow or prohibit the sender of the link to delete this type of shared file. Others section
• Restrict Access To Distribution List: When a group selects inter-group permissions = Explicit bulk emails using a distribution list are restricted. One requirement is to select this checkbox. For more information, see . Group Properties > Distribution tab.
• Auto assign licenses to new users: The system assigns a license to each new user. • User belong to Private/Local network: Are users of this policy on a local network.
- Click Next. The policy parameters page appears.
New Policy Permissions
Figure 67: New Policy > Permissions
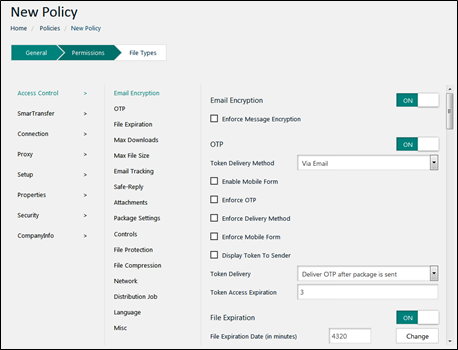
- Configure the policy parameters according to the requirements of the group/s you want to connect to the policy.
Info: Refer to this link to learn about the available policy parameters: Safe-T SDE Policy Parameters.
- When you finish configuring policy parameters, click Next. The file types page appears.
New Policy File Types
Figure 68: New Policy > File Types
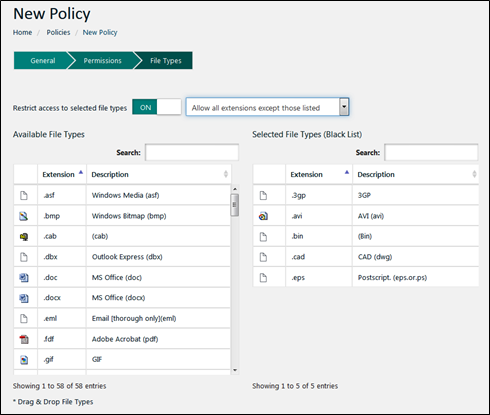
• Restrict access to selected file types: Select either a white list or black list filter.
o Allow only the listed extensions.
o Allow all extensions except those listed.
• Available file types: The global table of file types appears on the left side. Create the policy-specific filter by dragging and dropping file types from the global to the filter table.
When you are done, click Save. Your new policy is completed.
Info: If you edit a policy while you have the Safe-T web portal open, for the changes to take effect log out of the web portal session and log in again.
Edit Policy Permissions
In Safe-T SDE you can grant to an LDAP user or group permissions on all of a certain type of Safe-T object. For example, permissions to add, modify, remove, or view all Safe-Spaces, policies, groups, users, roles, external tools, etc. For more information, see How To Create And Apply Roles.
This section describes how you can grant permissions on specific policies.
Note: Safe Spaces, policies, and groups are the only Safe-T objects that support granting permissions on specific Safe-T objects.
To learn how to grant permissions on a specific group, see the steps described here: How To Grant Permissions on Specific Safe Spaces, Policies, and Groups
Disable a Policy
If you disable a policy, the groups assigned to the policy are prohibited from interacting with Safe-T SDE.
You can do either of the following:
• Disable a policy for all of its connected groups.
• Disable a policy for specific group.
To disable a policy for all groups:
- In the navigation pane, click Properties.
- Open the policy properties you want to toggle On/Off.
Figure 69:Toggle Policy On/Off For All Connected Groups
- Toggle the policy either On/Off.
- Click Save.
All groups assigned to the policy are blocked from interacting with Safe-T SDE.
To disable a policy for specific groups:
- In the navigation pane, click Properties.
- Open the policy properties you want to edit.
- Ensure the policy is toggled On.
- In the Assigned Groups list, click each group you want to toggle from Active/Inactive.
- Click Save.
The image shows two active policy to group connections and one inactive connection
Figure 70:Toggle Policy On/Off For Specific Connected Groups
How To Create And Apply Roles
A Role is a named collection of Safe-T SDE objects and permissions. You can use the Safe-T SDE Administration console to create roles that correspond to IT jobs that exist in your enterprise.
Example: You can create a role called: Help_Desk. The help desk user may be responsible for tasks such as creating new users and resetting passwords, but not managing Safe Spaces or policies.
Tip: Safe-T SDE supports flexibility and granularity in granting group and user permissions.
Info: Administrators have full permissions on all Safe-T SDE objects. The Safe-T SDE Administration console provides a separate method to create administrators. For more information, see Creating New Administrators.
The non-administrative roles you create should contain a subset of the authority granted to administrative roles: access to fewer Safe-T SDE objects and/or reduced permissions on those objects.
Roles Web Page
- In the Administration console navigation pane, select Roles. The Roles web page appears.
Figure 71:Roles Web Page

In the Roles web page, you can do the following:
• Create a new Role.
• Edit a Role.
• Edit Permissions of groups and users enabling them to perform actions on the Role object (e.g. create or modify a Role).
• Create a new Administrator’s group or user.
• Determine via screen tips which groups and users have permissions to perform an action on various objects and the name of the role by which the permission was granted.
Tip: In the Roles web page, if you hover your mouse over a green rectangle a screen tip displays the users and groups that have a permission on an object.
The figure below shows the two groups read.only and marketing have an undefined permission on Safe Spaces they were granted using the System Configuration role.
Figure 72:Roles Web Page

As an administrator, if you want more information about the users and groups that have permissions on Safe Spaces, open the object’s Edit Permissions web page. In this example open the Safe Spaces web page > Edit Permissions page.
You can see the Marketing group is selected and via the System Configuration role it has full permissions on Safe Spaces.
Figure 73:Determine Permissions Granted
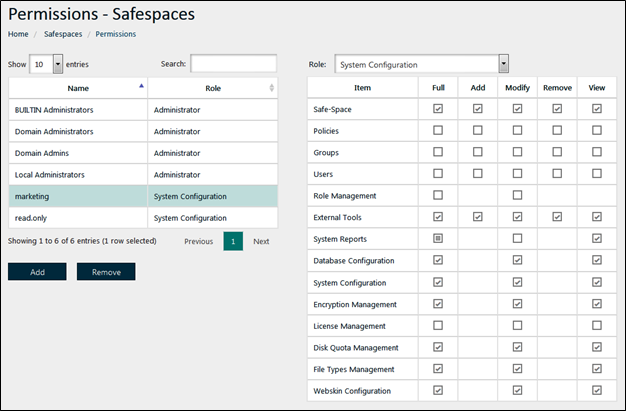
About Permissions
This table describes the available permissions on Safe-T SDE objects.
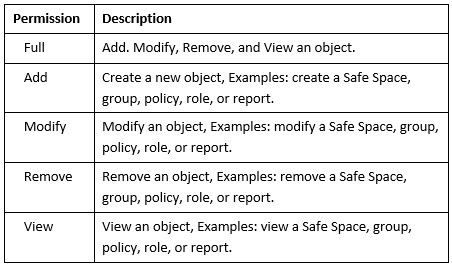
Tip: Safe-T SDE also supports another type of permissions: Safe Space permissions on files. See, Safe Space > Security.
About Objects
There are two types of objects: Objects that are managed in the Safe-T SDE Administration console, and objects that are managed in the Safe-T SDE Configuration tool.
Note: Each object managed in the Safe-T SDE Administration console has its own Edit Permissions web page. Objects managed in the Safe-T SDE Configuration tool do not have their own Edit Permissions web page.
If an object does not have an Edit Permissions page, use the Roles Edit Permissions web page to grant permissions on those objects.
If you grant a user permission on objects in this list, the user performs allowed actions with the Safe-T SDE Administration console.
Objects Managed With The Safe-T SDE Administration Console
• Safe-Spaces
• Policies
• Groups
• Users
• Role Management
• License Management
• File Types Management
• System Reports
Note: When you grant a group or user permissions on the objects listed above, you need to follow these essential steps:
Step #1: Create or use an existing role that contains a permission for the object. For example, a role called Policy_Manager can have full permissions on Policies and view permission on File Types Management. Policy definitions can optionally include a file types filter.
Step #2: In the web page for the object, in this example Policies, click Edit Permissions.
Step #3: In the Edit Permissions for Policies web page, connect the group or user to the role. Click Save.
Step #4: In the web page for the object, in this example Settings > File Types, select Edit Permissions.
Step #5: In the Edit Permissions for File Types web page, connect the group or user to the role. Click Save.
If you grant a user permission on objects in the list below, the user performs allowed actions with the Safe-T SDE Configuration tool.
Objects Managed WIth The Safe-T SDE Configuration Tool
• External Tools
• Database Configuration
• System Configuration
• Encryption Management
• Disk Quota Management
Note: The objects listed above do not have their own Edit Permissions web page. For the objects listed above, use the Edit Permissions page for Roles to connect groups and users to the objects.
Step #1: Create or use an existing role that contains a permission for the object. For example, a role called Externaltoolsmanager can have full permissions on External Tools, System Reports, System Configuration, and Encryption Management.
Step #2: In the web page for Roles, select Edit Permissions.
Step #3: In the Edit Permissions for Roles web page, connect the group or user to the role. Click Save.
About Object Dependencies
Consider if there are any dependencies when you grant users permissions on objects.
Examples:
• A user with Add permission on Safe Spaces should have at least View permission on policies. In the Safe Space Security details section, there is a drop-down list with policies you can optionally choose from to connect to the Safe Space.
• A user with Add permission on groups should have Add permission on users, and a least View permission on policies, Safe Spaces, and reports (for the history section).
• A user with full permissions on policies should have at least View permission on File Type filters because policy definitions can optionally include a file types filter.
Principle Of Least Privilege
The procedures for granting permissions in Safe-T SDE are designed to facilitate the principle of least privilege. You can use the Safe-T SDE Administration console to grant users the minimum possible authority to perform their jobs.
Info: Safe-T recommends you create a diverse set of granular roles to meet the precise access control requirements of your enterprise.
Active Directory User Requirement
A person who is not an Active Directory user, cannot log into the Safe-T SDE Administration console. Permissions can be granted only to Active Directory users.
One exception to the above rule: Local administrators can log into the Safe-T Administration Console and they have full permissions on all Safe-T objects.
How To Create A New Administrator
This section describes how to create administrators using the Safe-T SDE Administration console. You do not have to create a role: Administrator.
Info: Safe-T SDE administrators have full permissions on all Safe-T SDE objects.
To create a new administrator:
- In the Administration console navigation pane, select Roles. The Roles web page appears.
Figure 75:Roles Web Page
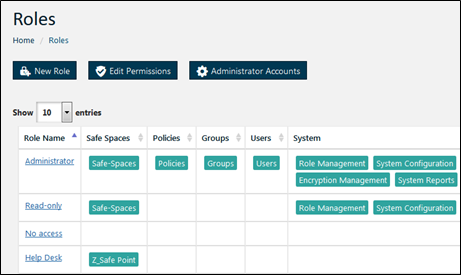
- Click Administrator Accounts. You can see a list of the existing administrators.
Figure 76:List Of Administrator Accounts

- Click Add. A pop-up window appears. In the pop-up window, search for LDAP users or groups.
Figure 77:Grant An LDAP Group Administrator Permissions

- Select the group or user you want to grant administrator permissions and click Add selected.
- In the Roles web page, click Save.
- You can verify the LDAP group (or user) was added as administrator(s) in two ways:
• Open the Administrator window and verify the new administrator is listed.
• In the Roles web page Administrator row, hover your mouse over an administrative object and find the LDAP group or user listed in a tool tip.
Figure 78:Verify An LDAP Group Has Administrator Permissions
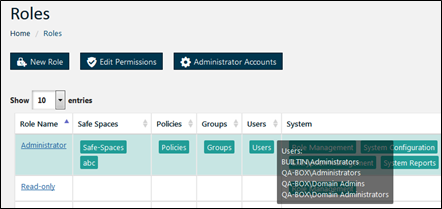
Configure Group Permissions Then User Permissions
Info: Best Practices: Safe-T recommends you assign to groups a set of permissions defined in a role. After that grant to specific users exceptions, that is additional or reduced permissions.
Example: Create an ITStaff role and assign it to the group ITStaff. In this example, the IT_Staff role you created does not include a permission to manage licenses.
However, you decide a single IT_Staff user should be able to manage licenses. Edit the permissions for that user and grant the managing licenses authority.
How To Create A New Role
This section describes how to create a new role.
Tip: You do not have to create a role: Administrator.
A role definition defines the permissions a user connected to that role can be granted. To create a new role:
- In the Administration console navigation pane, select Roles. The Roles web page appears.
- Click New Role. The New Role web page appears.
- Enter a name (e.g. IT_Staff) for the role and select the permissions you want to grant.
Figure 79:New Role Permissions
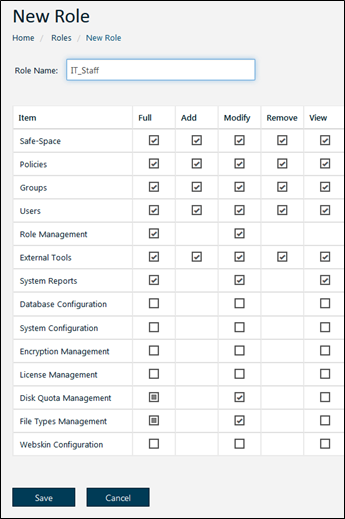
- Click Save. In the Roles web page, the new role appears:
Figure 80:The New Role Is Listed

How To Grant A Group Permissions Defined In A Role
Info: These steps are not applicable for creating administrators. For more information, see How To Create A New Administrator
Tip: Best Practices: Safe-T recommends you assign to groups a set of permissions defined in a role.
After that grant to specific users exceptions, that is additional or reduced permissions. This example describes how to grant a group the permissions defined in the IT_Staff role.
To grant a group IT_Staff role permissions:
- Create the role you want to use, for example IT_Staff. This role was created in a previous section. See, How To Create A New Role.
Note: You need to configure each object’s Edit Permissions web page separately if permissions on an object are granted permissions in the role IT_Staff.
For example, in the ITStaff role the first object the role grants permissions for is Safe Spaces. In the Safe Spaces Edit Permissions web page you connect the ITStaff role with the group.
The requirement to use the Edit Permission web page of each object to connect a role to a group or user promotes care and diligence. This procedure is designed to result in a more secure network.
Info: Each object’s Edit Permissions web page can grant permissions only for that object. For example, the Policy Edit Permissions web page can only be used to grant permissions on policies.
- In the Safe Spaces web page, click Edit Permissions.
Figure 81:Edit Permissions
- In the Edit Permissions web page, select the Groups option button and search for the group you want to grant ITStaff role permissions. In this example, we connect the ITusers group to the IT_Staff role.
Figure 82:Edit Permissions

- Click Add selected.
- In the Name and Role table, select the group you added.
- In the Role drop-down list select the IT_Staff role.
Figure 83:Connect Group, Role, And Permissions

- Inspect and verify the row for the object permissions you are granting to the user are correct.
- Click Save.
- Verify on the Roles web page the group has been granted the permissions you assigned. In the row for the role, examine the screen tips on each object.
[You must now loop back and repeat the configuration process on each object in the IT_Staff role]
- Perform steps #2 through #9 for each of these objects: Safe Space, Policies, Groups, Users, Roles, Reports, and File Types filter.
Note: In the IT_Staff role there are two remaining objects you need to configure: External tools and Disk Quota Management that do not have their own Edit Permissions web page.
The objects without their own Edit Permissions web page you configure in the Roles Edit Permissions web page as follows.
- In the Administration console navigation pane, select Roles. The Roles web page appears.
- Click Edit Permissions. The Edit Permissions Roles web page appears.
- Click Add. A pop-up window appears. In the pop-up window, search for the IT_users group.
- Select the group and click Add Selected.
- Select ITusers and in the Role drop-down list select the role: ITStaff.
Figure 84:Grant Permissions To Objects With No Edit Permissions Web Page

- Click Save. You have now completed granting the group ITusers all permissions contained in the role ITStaff.
How To Grant A User Permissions
Demo.User is a member of the group ITusers which has permissions defined in the role ITStaff. We now want to grant Demo.User a permission not included in the role IT_Staff.
This example shows how to grant to a single member of the group IT_users permission to manage licenses.
To grant a user permissions:
- In the Administration console navigation pane, click Settings. The License Management web page appears.
- Click Edit Permissions.
- Click Add and in the pop-up window select the Users option button and search for the user who is a member of IT_users. This is the user you want to grant License management permissions.
Figure 85:Search For User To Grant Permissions
- Click Add Selected.
- In the Permissions License web page, select Demo.User and in the role drop-down list select the role: License Management.
- Click Save. Demo.User who is a member of the group ITusers has the permissions granted in the role ITStaff. However, Demo.User can now can also manage licenses by obtaining the permission included in the role: License Management.
Figure 86:Connect A User To A Role

How To Grant Permissions on Specific Safe Spaces Policies and Groups
This section describes how you can grant permissions on specific Safe Spaces, policies, and groups.
Note: Safe Spaces, policies, and groups are the only Safe-T objects that support granting permissions on specific Safe-T objects.
Previously we described how to grant users or groups permissions on all of a certain type of Safe-T object. For example, permissions to add, modify, remove, or view all Safe-Spaces, policies, groups, users, roles, external tools, etc.
The following example describes how to grant permissions on one specific policy called: Standard.
We want to allow a group called Help Desk to have the permissions granted in the role IT_Staff but only for the Standard policy. The Help Desk will not have permissions on any other policy.
Note: Use the same steps to grant permissions on a specific Safe Space or group.
To grant permissions on specific objects:
- Open the Standard policy properties web page and expand the Permissions section.
- Click Add. A pop-up window appears.
Figure 87:Find Active Directory User or Group

- Search for the LDAP user or group you want to grant permissions. Click Add Selected.
- In the Name - Role table, select the IT_Staff role.
In this example, we grant permissions to the group Help Desk. Members of the Help Desk group will have IT_Staff permissions to perform operations on the Standard policy, but no other policy.
Figure 88:Help Desk Group With IT_Staff Permissions on Standard Policy

How To Generate Reports
The Reports window enables you to view and export Safe-T SDE Server events by configuring a set of filters.
Report Example
This is an example of a History type report.
Figure 89:History Report
Report Window
• ID: Displays the ID for the action.
• Event Action: The type of the operation, for example an email was sent or a file was uploaded.
• Package ID: Identifier for an email message and its file/folder attachments, or any zipped group of files.
• Sender \ Recipients: Displays the sender or the recipient name.
• Status: Displays the status of the selected operation.
• Pkg/Type Name: Type of the package, for example Outlook email message.
• IP address: Displays the IP address the user has connected from. The last hop before accessing the Safe-T SDE server).
• File Size: Displays the file size of the report.
• Date: Displays the date the record was generated.
Create A New Report
- In the navigation pane, select Reports. A Reports web page appears.
- Select and configure filter parameters using the descriptions below.
- Click Run to generate the report
Figure 90:Configure A New Report

Report type and events:
Note: “None” means no filter applied. For example, if you leave the default “None” for Safe Space, that filter will include all Safe Spaces.
• Report Type: Set the type of filter for the report. The filters are: history, users, groups, policies, Safe Spaces, packages, and history.
• Show In Report: Select Events, and depending on the Report Type you selected, other options may display. For example, if you select Report Type is Safe Spaces, the Show In Report field provides an option to display Safe Spaces users.
• Event Type: Set the type of event recorded in the report. Event multi-select is available only with History report type. The filters are:
o upload file
o upload package
o upload failure
o download
o download failure
o share file
o send email
o send email failure
o send SMS
o send SMS failure
o Max file size
o File type
o Create folder
o Create folder failure
o Delete file
o Delete file failure
o delete folder
o delete folder failure
o login
o login denied
o login failure
• Groups: Filter the report data by the selected group.
• Safe Spaces: Set the report filter to display a selected Safe Space.
• Policies: Filter the report data by the selected policy.
• Package ID: Filter the report data by the defined Package ID.
• Inactive users: Choose if the report should include only active users, or all users.
• From and to: Set the start and end date for collecting the report data.
• Username: Filter the report data by the specified user name.
o Search by: Set the search mode (like, equals, starts with, ends with).
• Recipient: Filter the report data by the specified email recipient.
o Search by: Set the search mode (like, equals, starts with, ends with).
• Run: Generates the report using the parameters you set.
After you generate a report you can do the following:
• Resend Message and Reset OTP. Use the two links on the right-side of a row that displays data for an email action.
• Export or print the report:
o Export to PDF: Export the report to PDF file.
o Export to Microsoft office Excel: Export the report to Excel file.
o Print: Sends the report to a printer.
Schedule A Recurring Report
You can schedule the system to automatically generate reports. For example, you can schedule an events history report to be generated and emailed to you at 5:00PM daily.
You can configure an automatically generated recurring report by following the steps in this section: .External Tool #22: Activity Report
How To Audit Administrative Actions
The audit feature enables you to view a table of recent actions (i.e. events) performed by an administrator. For example, create a Safe Space, a user, a role, update a policy, etc.
You must log into the Safe-T SDE admin web UI as an administrator.
Info: You can determine who are the admin web UI administrators from this list: Roles > Administrator Accounts.
This is an example list of administrator accounts:
Figure 91:List Of Web UI Administrators

Info: If you log into the admin web UI as a user who is not an administrator, the ‘Audit’ icon in the navigation pane will not be visible.
To view administrative actions:
- In the navigation pane, select Audit. A historical table of administrative actions appears.
Figure 92:Audit Web Page

Audit Window
• Administrator Account: The name of the administrator who performed the action.
• Event: The type of operation. For example: create, update, delete, assign, unassign.
• Category: The type of Safe-T object. For example: Safe Space, user, group, policy, role, report.
• Details: The specific name of the Safe-T object.
• Event Time: The time and date the action occurred.
• Status: The status of the operation.
Filters
• Filter By Date: Set a custom From and To time period
• Filter By Events And Categories: Select events and categories you want displayed in the ptable.
How To Block Access To Sent Packages
An administrator can block an email recipient from accessing file attachments a user emailed with the Outlook plug-in or Safe-T web portal.
Info: There are different administrative actions available depending on whether the email is sent to a single recipient or to multiple recipients.
[The email and package is sent to a single email recipient.]
To block a single email recipient from accessing a package after the recipient downloads the package one time:
- In the navigation pane, select Reports. A Reports web page appears.
- Click the row of the email sender whose package you want to block. You can determine the row to select by examining the attributes such as: sender name, time/date sent, package ID, IP address, and envelope icon.
A window similar to this appears:
Figure 93:Report: Package And Message Header

- Click the Package Status button.
A window similar to this appears:
Figure 94:Package Status Single Email Recipient

- When the recipient downloads the package, an administrator can block further access by toggling either of the package status buttons from Active to Inactive.
[The email and package is sent to a multiple email recipients.]
To block all email recipients from accessing a sent package:
- Follow the same steps as described above. However, toggle the main Package Status button to Inactive.
If you do this before any recipient downloads the package, you completely block access to the files.
Info: If an email is sent to exactly one recipient, you cannot block that recipient from accessing the package one time.
[End users working with the Outlook plug-in]
The steps above describe actions an administrator can take in the Reports web page to block package access.
However, Outlook plug-in end users can also take actions on packages they send. In the Outlook plug-in Package Properties end users can add, replace, and delete file attachments. They can perform these modifications even after the file attachments have been accessed by the email recipient.
The relevant policy parameters to configure for Outlook plug-in end-users.
Table 2 Policy Parameters To Enable End Users

For more information, see Safe-T Outlook Plug-in User’s Guide.
How To Connect to the Organization’s SMTP Server
This section describes how to configure the IIS SMTP Virtual Server and the SMTP external tool to enable Safe-T SDE to send emails to the organization’s SMTP server.
The two use cases described below differ according to the organization’s SMTP server authentication method.
• If the SMTP server does not require authentication, Safe-T SDE can connect directly.
• If the SMTP server requires Windows authentication, Safe-T SDE uses the built in IIS 6.0 SMTP virtual server to authenticate to the organization’s SMTP server.
SMTP Server: No Authentication
In this section, it is assumed your organization has deployed an MTA that does not require authentication. For this use case connect from the Safe-T SDE server to the MTA bypassing the IIS SMTP Virtual Server.
Do the following:
- In the IIS SMTP Virtual Server, leave both the 1) Connection and 2) Relay values at their default value: 127.0.0.1 IIS 6.0 Manager > SMTP Virtual Server Properties > Access tab
- Configure the Safe-T SDE external tools.
Using the SDE Configuration tool: Tools > External Tools > Email and Text Messaging Service Role > SMTP.
• SMTP Server > enter the MTA IP address.
• SMTP Server > enter the SMTP port.
• Click Save in the Extensions dialog box.
• Click Save and Deploy in the Safe-T SDE External Tools services dialog box.
SMTP Server: Windows Authentication
In this section, it is assumed your organization has deployed an MTA that requires Windows authentication.
Do the following:
- Leave the SMTP external tool with these default values:
• SMTP Server: 127.0.0.1
• SMTP Port: 25
- IIS 6.0 Manager > SMTP Virtual Server Properties > Delivery tab Set both the 1) Connection and 2) Relay values to the MTA IP address.
How To Enable Sending SMS/OTP Messages
This section describes how to configure the system to send SMS/OTP verification codes to email recipients.
By default, email recipients who are not registered users in Safe-T SDE access secure email message/attachments by entering in the Safe-T web portal an OTP sent to them either by SMS or in a separate email.
Note: If you want you can force registered users to use OTPs as a security credential instead of logging in with their Windows domain credentials.
Prerequisite: Contract with a third-party mobile carrier that can send SMS/OTP verification codes, depending on your needs, globally or in the locales in which your emails will be sent.
An example of a mobile carrier that can supply SMS/OTP verification codes: www.clickatell.com.
Info: The carrier will supply you with a URL that typically contains these components: SMS provider user name, password, email recipient’s mobile phone number, sender’s email address, SMS message.
In addition to the above wireless carrier prerequisite, enabling SMS/OTP requires you to complete these four steps:
- Configure external tool #16: Mail-Relay and OTP Delivery Configuration. The OTP delivery method must be set to HTTP/s. For more information, see External Tool #23: Mail-Relay and OTP Delivery Configuration.
- Configure external tool #18: HTTP/s (Web Service For SMS/OTP). You must set the URL you obtain from your SMS/OTP mobile provider. For more information, see External Tool #25: HTTP/s (Web Service For SMS/OTP)
- Configure the following policy parameters. For more information see, How To Create Policies.
Table 3: Policy Parameters For Configuring OTP

- If you want configure the enforce OTP checkbox: Groups > Select the group you want to configure > Security & Distribution Group section > Select a group with Security Group = True.
In the group’s row, click the properties icon. The following screen appears:
Figure 98: Group Properties: Enforce OTP

- If you select the checkbox to Enforce OTP, when members of the group send email to registered Safe-T SDE users, the email recipients are sent OTP verification codes.
If you do not select this checkbox, registered Safe-T SDE recipients access secure content using their Window domain login credentials.
Info: The setting in the group properties enforce OTP checkbox overrides any conflicting OTP configuration you set in policy parameters.
For example, if you set the policy parameters Enable/enforce OTP to ‘false’ but select the above group properties enforce OTP checkbox, the group’s email recipients, both registered and not registered, all are required to use OTPs to access secure content.
Email Path With SMS OTP
This section describes the path an OTP takes:
- Safe-T user sends an email with file attachments using the Outlook plug-in or Safe-T web portal.
- The file attachments are uploaded to the Safe-T SDE Outlook Safe Space.
- The email is sent through the Microsoft Exchange Server.
- Safe-T SDE notifies the third-party SMS/OTP provider what is the phone number of the email recipient.
- SMS/OTP provider sends OTP to email recipient.
- The recipient clicks the email Secure Content link in the email message and uses the OTP to authenticate to Safe-T SDE.
How To Set An Email Address For Receiving Notifications
The system notifications are sent to the email address in the SMTP Delivery Service external tool’s email address field.
Figure 99: SMTP Delivery Notifications Email Address
How To Customize the Safe-T IIS Website
You can customize the appearance of your organization’s IIS website: Safe-T web portal for end users. This customization can be done globally or at the level of groups. You can provide each of your organization’s groups a different look and feel on the Safe-T web portal login web page.
Tip: The administrator who performs the IIS website customization should be familiar with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and graphic design.
Info: Before you modify any files that affect the web UI, back up the IIS folder ui_api so you can restore the unmodified files if needed.
Default and Group Webskins
Safe-T SDE IIS website supports default and group webskins. The Default webskin defines the appearance of the IIS website for all groups. You can override the appearance of the website by modifying either the default global webskin or separate group webskins.
Customizing the Default Webskin
The default global webskin defines visual layouts and color schemes globally for all Safe-T SDE IIS website pages including: log in, logged out, secure content download, file upload and management, and web-based email pages.
The default webskin includes files for customizing page elements such as:
• Background colors and images
• Control colors
• Headers and footers
• Display text
To customize the default webskin:
- In the Safe-T SDE server, open the IIS Web site files folder for the default webskin.
Note: The IIS Web site files folder for the default webskin is located in the Safe-T SDE installation path here:
C:%ProgramData%\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api\WebSkin\DefaultWebskin
Figure 100: Default Webskin Folder

- Edit the HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files according to your customization needs. Your modifications will be used as the new default global webskin.
Customizing a Group Webskin
A group webskin defines visual layouts and color schemes for Safe-T SDE website pages viewed by members of a single group.
Info: Your organization can display Safe-T SDE web pages customized by various business departments, geographic locations, languages, or other reasons such as a seasonal holiday.
Before you can customize a group’s webskin you must create the Safe-T SDE group. When you create a group, Safe-T SDE copies the contents of the DefaultWebskin folder into a folder under WebSkin having the name of the group.
For example: C:\ProgramData\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api\WebSkin\Organizers
When you customize a group webskin, as shown in the following steps, you start with the default web skin files as the starting point for your customizations.
To customize the default webskin:
- In the Safe-T SDE server, open the IIS Web site files folder for the group webskin you want to customize.
Note: The IIS Web site files folder for the default webskin is located in the Safe-T SDE installation path here:
C:%ProgramData%\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api\WebSkin<Group Name>
- Edit the HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files according to your customization needs.
Example: Customize The Safe-T Login Web Page
This section describes how to customize the logo and background images of the default Safe-T login web page.
Note: Some elements of the Safe-T website cannot be customized without help from Safe-T Support. For instance, the login HTML page source is generated dynamically using active server pages: login.aspx. If you try to modify the HTML page source, any changes you make will be lost when you refresh the page in your browser.
Tip: Backup all the files you plan to modify so if needed you can restore the login web page to its default appearance.
In this example, backup this folder:
C:%ProgramData%\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api\WebSkin\DefaultWebskin
This is the default Safe-T login web page.
Figure 101: Safe-T Web Portal

To customize the company logo and background images:
- Open the Safe-T login web page in a Chrome browser.
Note: We use Chrome to access its built-in development tools. In this example, we want information about the logo and background images.
- To open the Chrome Developer tools, right-click anywhere on the web page and click Inspect. The Chrome Developer tools appear. Changes you make using the Chrome Developer tools are non-persistent.
Figure 102: Safe-T Web Portal - Chrome Developer tools

- In the object tree, expand the folders. You can see the file names of the images.
If you select bg01.jpg in the tree, a thumbnail image displays. The height and width of the image in pixels are also noted at the bottom of the pane: 1920 x 180.
Figure 103: Change The Background Image

- Locate the Logo.png and bg01.jpg files in the folder DefaultWebskin that resides in your Safe-T SDE server installation path. The changes you make to these server files are persistent.
- With a graphics editor, customize the image files and without changing their file names save them to the Default Webskin folder.
- Close the development tools and refresh your browser.
The following image is an example of the Safe-T login web page with customized logo and background images:
Figure 104: Customized Web Portal

Advanced Server Configuration
This section describes Safe-T SDE server advanced configuration parameters. These configuration values usually should be left with their default values.
Several configuration parameters overlap group policy parameters. In these cases, as noted in the descriptions below, the overlapping parameter will either override or set a default value across the similarly named group policy parameter.
Info: For more information, contact Safe-T Support.
To change a configuration parameter:
- In the navigation pane, select Settings.
- Click the Config link. The Configuration web page provides access to advanced settings for the Safe-T SDE server.
- Make the changes you want then click Save.
You do not have to activate your configuration changes immediately.
- Restart the Safe-T SDE Enterprise Windows service to activate your configuration changes.
Caution: To activate your configuration changes, you need to restart the Safe-T SDE Enterprise Windows service. Do this during a planned, scheduled maintenance period. When you restart the Safe-T SDE Enterprise Windows service all current Safe-T SDE server communication sessions are dropped.
The section below describes the Safe-T SDE server advanced configuration parameters.
System Parameters
This section describes the Safe-T SDE advanced configuration parameters:
Company Info
• Company Support Information: Displays Safe-T Data support email address.
Properties
• Max Threads For all Jobs: Set the maximum number of threads for each job.
• Is Print Debug Stack: Allow activating the Safe-T SDE server debug stack to provide more information printed to the logs. This option consumes more server resources.
• Cookies Persistent Max Expiry Date: Define the web session duration.
• Is Using COM Plus APP: Set if the Safe-T SDE server uses COM Plus application.
• Is auto Create System Directories and Windows Account: Allow automatic creation of the iSafe-T user. If set to Yes, the server creates the iSafe-T user at the next logon.
• Is Cache Active Directory Users Authentication: Is AD performing caching user authentication.
• Globalization Current Culture Name: Uses your Windows language locale setting.
• User Pass Mask: Set the format of the password generator used by the server in “create new user” form.
For example: A mask will generate passwords UC letter, LC letter, 4 digits. (e.g. Tn8103
• User Pass Min Length: Set the minimum user password length for the password generator.
• User Pass Default Expiry Days: Set the default expiry value in days for the user passwords.
• User Pass Allow Change: Set the default mode for allowing or preventing users to change their passwords.
Security
• Is Force Message Encryption: Set to enforce message encryption.
• Is Message Encryption: Set the default mode of message encryption.
• Total Number Of User Authentication Retries: Set the maximum number of wrong login retries before disabling user.
• Is Enabled Active Directory Secure Login For Recipients: Set the Windows Kerberos authentication method for all incoming packages.
IIS
• Secure Virtual Directory name: Set the name of the secure virtual directory.
• Built In Access Username: Set the username used by the Safe-T SDE Server to build the IIS website.
• Default Upload Buffer Size: Set the default upload buffer size. The value is set in KB.
• Default Download Buffer Size: Set the default download buffer size. The value is set in KB.
Reverse Proxy
• Is Reverse Proxy: Displays the Safe-T SDE server configuration setting for using reverse proxy.
• Is Force Secure Connection Over Session: Set the connection settings. In case the sender is connected via port 80, and sending an invitation, the link will send as HTTP and not as HTTPS. If set to Yes. all invitations set as HTTPS.
• Is Force IIS Host Over Session Host: System option for troubleshooting.
• IP Address Login Access Comparison: System option for troubleshooting.
• HTTP Header Comparison: System option for troubleshooting.
• Domain List: The same value as set in Tools-> Domain List. OTP
• Token Format: Set the Token format. The value set in “#”.
• Token Case Sensitive: Set if the OTP token is case sensitive or not.
• Token Expire After: Set as a default for new policies the duration of the OTP validation time before the token expires.
• Is Force SMS for all Messages: Set if you want to enforce SMS delivery method for all OTP codes sent.
• Token Length: Set the length of the OTP sent to users.
Storage Configuration
• Show Hidden files: Set Safe-T SDE server configuration for hidden files.
• Allow Recursive Folder Delete: Allow deleting all sub folders\ and files under the selected folder.
Messages
• Body Message Encryption: Set the body message of the email which replaces the original body of the message. The value is set in HTML format.
• Verification Code via SMS Default Message: Set the SMS message format sent by the Safe-T SDE server. Safe-T Verification Code: {0} [Id: {1}]
You should modify only this: “Safe-T Verification Code: ”
• Verification Code via Email Default Message: Set the Email message format sent by the Safe-T SDE server. Safe-T Verification Code [ Id: {0} ] You should modify only this: “Safe-T Verification Code: ”
• OTP Verification Code via SMS to Email Gateway: Set the SMS to Email message format sent by the Safe-T SDE server.
Safe-T Verification Code {0} [ Id: {1} ]
Note: You should modify only this: “Safe-T Verification Code: ”
Utilities
• Outlook: Name of the Outlook Plug-in setup file. Default: Install_Outlook.msi
• Client: Utilities.zip
• Safe Explorer IE: SmarTransfer.exe
• Is Smar Transfer Enabled: No
Logout Redirects (Enter absolute paths)
• Default Signout Redirect URL: The default redirect after users logout is the Safe-T web portal login page.
• Use Custom Redirect URL: Do you want to customize the next three redirect URLS?
Note: If the Default Signout Redirect URL field is empty and the Use Custom Redirect URL checkbox is cleared when an end user logs out they are redirected to the login page.
• Web Portal Redirect URL: Specify a redirect URL after users logout of the web portal.
• Safe Reply Redirect URL: Specify a redirect URL after email recipients logout of the Safe Reply web page.
• Secure Email Redirect URL: Specify a redirect URL after email recipients download secure content. System Events
• Is Use Admin Email Address for Notification: Set if the Safe-T SDE server uses the Admin user Email address to deliver Safe-T SDE notifications.
How To Manage Safe-T SDE Licenses
This section describes how an administrator can do the following:
• Request a license for end users.
• Activate the license.
• Assign licenses to groups and users.
Request and Activate License Overview {#request-and-activate-license-Overview}
On the License Management web page, you can request and activate a license.
- In the navigation pane, select Settings.
- Click Export to File > Export details of your license request to a local file.
- Email the license request file to Support@safe-t.com.
- If your request is approved, you will receive an email with the end users activation key.
- Click Import from File > Import the license activation key to Safe-T SDE server.
- Restart IIS and Safe-T SDE server.
Figure 105: License Management
Current License Information
In the License Management web page, create a license request by doing the following:
- Select the type of license request you want to create:
• User license: Request a license for a specified number of users. Be sure to enter the exact number of user licenses you want.
• Site License: Request a site license.
• Trial Period Extension: Request a trial extension period.
- Select Export to File.
- Browse for the license request file you exported.
- Copy the request file and email it to Support@safe-t.com.
Tip: If you click Send via Email, instead of Export to File, your request is sent automatically to Safe-T Support. In Outlook, you will not see a sent email for the license request. Info: If your license request is granted, Safe-T Support will email you a license key file.
How to Activate The Licenses
- Click the button: Import to File. A browse for window appears.
- Select your license key sent by Safe-T Support.
- Click Open.
- Restart IIS by doing the following: Start > Run > IISReset > OK.
- Restart Safe-T SDE server. Your license should be activated. You can verify the new license parameters in the license management table.
How To Assign Licenses To Groups And Users
You can assign licenses using several different methods:
• License Web Page: Assign licenses to users or groups.
• Group Properties Web Page: Assign a single group member a license.
• Policies Web Page: Auto-assign all users connected to a specific policy.
License Web Page
In the license web page, you can assign licenses to users or groups.
- Click License Management. A pop-up window appears.
Figure 106: Licenses: Select user or group
- In the tree directory, select a group or user, then click Apply.
• If you select a group and have a site license, all users in that group are assigned licenses.
• If you select a group and have a license for a limited number of user, you will see an error message if the number of users in the group is larger than the number of available user licenses.
Group Properties Web Page
In the group properties web page you can assign a license to a single user.
Navigation pane Groups > Groups table > Select a group > Select a user to assign a license
Figure 107: Licenses: Select a Single Group Member

Policies Web Page
In the policies web page you can auto-assign a license to a user.
- Open the policy for which you want to enable auto-assign user licenses.
- In the Policy’s Other section, select the checkbox:
Figure 108: Auto-assign License Based on Policy

- Click Save.
How To Do Tasks List
This section provides a list of How To links. Each How To section describes steps for performing a specific administrative task.
• How To Use This Guide
• How To Stop The Safe-T SDE Server
• How To Deploy The End User Clients
• How To Use External Tools
• How To Monitor Any Folder
• How To Edit An External Tool Schema
• How To Create New Users
• How To Create Safe Spaces
• How To Display All Safe Spaces
• How To Manage Encryption Keys For Shared Safe Spaces
• How To Enable File Type Filtering
• How To Create An Outlook Archive Safe Space
• How To Create Policies
• How To Create And Apply Roles
• How To Create A New Administrator
• How To Create A New Role
• How To Grant A Group Permissions Defined In A Role
• How To Grant A User Permissions
• How To Grant Permissions on Specific Safe Spaces, Policies, and Groups
• How To Generate Reports
• How To Connect to the Organization’s SMTP Server
• How To Enable Sending SMS/OTP Messages
• How To Set An Email Address For Receiving Notifications
• How To Customize the Safe-T IIS Website
• How To Manage Safe-T SDE Licenses
• How To Assign Licenses To Groups And Users
Deployment Options
This section provides information on these deployment architectures:
• Standard deployment.
• Two companies sharing a Safe Space.
Tip: Safe-T SDE supports a wide range of deployment topologies. For more information, contact Safe-T Support.
Standard Deployment
This section described a standard Safe-T SDE server deployment in an enterprise. The sender’s message and file attachments are routed through Safe-T SDE.
The email recipient outside the LAN downloads the message using a secure channel from encrypted storage handled by Safe-T SDE. The recipient typically uses an SMS verification code to authenticate.
Figure 109: Safe-T SDE Standard Deployment

Two Companies Share a Safe Space
This section describes a deployment option enabling two companies to share a Safe Space.
Solution objectives
Two companies “A” and “B” use Safe-T SDE in their organizations. They are business partners and exchange many documents as they implement their daily work flows. The companies want to do the following:
• Grant to one or more groups in each company permissions to share files using a common Safe Space. For example, permissions to view, upload, and download files.
• Enable company employees to access the shared Safe Space from their own separate company-branded Safe-T web portals.
Prerequisites
Each company “A” and “B” has deployed in their own environments an instance of Safe-T SDE. To implement the shared Safe Space solution:
- In either company “A” or “B” create a single Safe Space. For this example, company “A” creates the Safe Space called “Partners_Space”.
To learn how to create a Safe Space, follow the steps described here: How To Create Safe Spaces.
- In company “A” create a Safe-T SDE user with permissions to perform all operations on the Partners_Space. This service user will perform operations on behalf of users in company “B” who want to access the Safe Space.
For security purposes, the service user should have no responsibilities other than to access the Partners_Space on behalf of company “B”.
- Company “A” must provide to company “B” this information:
A) The name of the Safe Space which in this example is Partners_Space.
B) The Partners_Space UFID. This Safe Space ID value is on the Identity tab of the edit Safe Space wizard. Note: Do not select the Enhance Security Checkbox. See, Safe Space > Identity.
Figure 110: Safe Space UFID

C) Company A’s Safe-T SDE server IP address or domain name.
D) The service account user name and password.
- Company “B” starts the new Safe Space wizard to create a connection to Company A’s Partner_Space.
- In the General tab > name field enter: Partners_Space.
- Enter a description of the Safe Space.
- Click Next. The Connection tab appears.
Figure 111: Connection Details

• Type: Select Safe-T Box
• Path: Enter ‘\’
• Credentials: Select the checkbox: Enable.
• Server\Domain Name: Enter the company “A” IP address or host name.
• Login: Enter the service account user name followed by ‘\’ then the UFID.
• Password: Enter the service account password.
• Use secure connections only: Select this checkbox.
Info: When you run the Safe Space creation wizard it does not create a new Safe Space when the connection type is Safe-T Box.
- Click Next. The Security tab appears.
- In the Security tab, add and configure permissions for all groups and users you want to grant access to the Partners_Space.
- Click Next. The Identity tab appears.
- In the Identity tab, enter the UFID of the Partner_Space.
- Click Next. The Advanced Settings tab appears.
- Fill out the Advanced Settings tab, using the instructions presented here: Safe Space > Advanced Settings
- Click Finish.
Users are now able to access the Partner_Space using the Safe-T web portal of company “A” or “B”.
How To Schedule Jobs To Upload And Download Files
This section describes how you can automate tasks to upload and/or download files from a folder on your file system to a Safe Space or from a Safe Space to a folder on your file system.
Prerequisites
Create a folder on your file system and a Safe Space.
To create a scheduled file upload/download job:
- In the main Safe-T SDE main window, click Tools > external tools.
- Click System Tools > Job Scheduler.
Info: The default Job Scheduler entry may be named: File Move Scheduler. If that is the case, in the properties window described below, rename it: Job Scheduler.
Figure 112: Job Scheduler External Tool
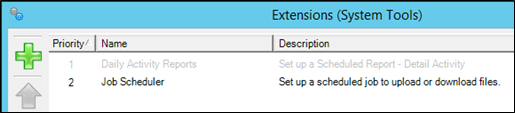
The Job Scheduler external tool window appears.
Figure 113: Job Scheduler Properties Window

[Schedule a date/time and recurrence trigger.]
The schedule trigger is an event that causes the job to be executed.
- Click the icon on the right side of the Schedule Trigger field.
A window appears enabling you to configure a schedule trigger.
Figure 114: Configure Job Schedule Trigger
- Enter values for these parameters;
• Start Date: When the task will first run.
• End Date: When the task will stop running.
• Occurrence Time: The time of day the task will start to run.
• Recurrence Pattern: The frequency the task will run.
- Click OK. The job scheduler properties windows reappears.
[Now you are required to configure the task you want to automate.]
- Click Add Task.
Figure 115: Configure The Task You Want To Automate
- Enter values for these parameters:
• Task Name: Name of the task.
• Username: Registered Safe-T SDE user with permission to access the Safe Space.
• Password: Password of the above user.
- Click Validate User. If the user and password are valid the following message appears.
Figure 116

- Enter values for these parameters:
• Move Type: Select either ‘upload’ or ‘download’.
• Safe Space: Select the name of the Safe Space.
• Safe Space Item: (Optional) A path in the Safe Space to a file or subfolder.
- Click Validate Safe Space Item. If the Safe Space is valid the following message appears.

Enter a value for either of the following:
• Source Path: For file upload enter the location of the source files.
• Destination Path: For file download enter the location to the download files.
- Click OK.
- Click Validate location. If the Source path or Destination path is valid the following message appears.

- Run Task Now: You can run the task immediately. This feature is for testing and ignores the schedule trigger.
- Click Save then in the System Tools window click Save again.
- In the main external tools window, click Save & Deploy.
How Create Multiple Tasks
Info: You can add multiple tasks in the same Job Scheduler external tool window. However, all of the tasks will use the same schedule trigger.
If you want you can create multiple tasks with different schedule triggers. In the System Tools window, click File Move Scheduler to create a copy of the external tool. In its properties window enter a different name such as Job Scheduler_1.

Backup And Restore The Safe-T SDE Virtual Machine {#Backup-and-restore-the-safe-t-sde-virtual-machine}
This section describes best practices for backing up and restoring the VM on which you deployed your Safe-T SDE server. It is applicable to the following virtualization technologies:
• VMware vSphere
• Microsoft Hyper-V
Why You Should Create VM Backups
Your organization should create periodic, off-site, Safe-T SDE server VM backups. Maintaining backups is important because you want to quickly restore service availability to your end-users if the Safe-T SDE VM fails.
The Safe-T SDE server running on a VM is designed to be resilient. However, under certain limited circumstances the VM can fail and cause service down-time. System failure can occur because of a cyberattack, human error, equipment failure, or natural disasters such as fires, earthquakes, and floods.
Tip: A major Windows Server update can affect the operation of the Safe-T SDE VM.
Best Practices For Backup/Restore Safe-T SDE
The best practices backup/restore strategy is to do the following:
- Clone the Safe-T SDE VM.
- Backup the volatile data separately.
- Restore the VM from the clone.
- Restore the volatile data.
Info: The VM clone or other type of backup is a heavy and costly operation. There is no need to perform this operation more than once.
Note: VM snapshot must not be used as a backup file. If the base disks are deleted, the snapshot files are not sufficient to restore a virtual machine
VM Clone Backup
Create a full clone of the Safe-T SDE VM. The full clone must be unconnected to changes in the parent clone and must not share virtual disks with the parent virtual machine.
You can perform the cloning operation after you initially deploy the Safe-T SDE OVA, or after the Safe-T SDE server has been in operation.
Note: Hyper-V does not provide a clone feature. However, you can create a copy of a VM using the export command.
Backup Volatile Data
Create daily backups of the remote SQL server and specific folders enumerated below that hold volatile, frequently changing data.
Files You Must Separately Back Up
The following files must all be backed up to restore the Safe-T SDE server:
• Safe Spaces (local and remote)
• SQL database (local and remote)
The following folders:
• C:\Safe-T\data
• C:\ProgramData\Safe-T Enterprise
• C:\ProgramData\Tirminal Corp
Info: Organizations typically work with a remote SQL database and remote Safe Spaces.
Restore Full Safe-T SDE Operation
Restore the Safe-T SDE VM from the clone then restore the separately stored volatile files.
Frequency Of Volatile File Backups
This section refers to the frequency your site backs up the volatile data.
In progress data exchanges (file uploads/downloads) and incomplete administrative configuration changes cannot be restored from backups. You must minimize the number of incomplete transactions you back up.
Implementing a time interval between your backups (e.g. weekly, daily) that is less frequent than real-time, continuous backups, means if you need to restore the system from your backup files there will be a loss of data. Changes since the most recent backup are not stored and cannot be recovered.
Tip: Safe-T recommends using continuous or daily backups of all volatile files noted above.
Off-Site Backups {#off-Site-backups}
Your production VM should ideally reside in a different physical location than your backup files. If there is a local natural disaster event such as an earthquake or fire, you will be able to restore service using your remotely stored backups.
Test Your Restore Procedure
If you do not test restoring service from backup files, if a disaster strikes, you might discover you have implemented incorrect procedures.
Implementing High VM Availability Using Failover Clustering
Failure of a virtual server on which your Safe-T SDE VM runs can cause service down time. VSphere and Hyper-V can be configured to use a multi-node server cluster that in the event of a host failure restarts the VM on an alternative clustered host.
Reference Section
This section provides supplementary information on certain topics.
Policy Parameters
This section provides supplemental information on policy parameters you can configure. As a generally applicable rule:
• Enable: Sets a default value for a parameter a user can modify.
• Enforce: Sets a default value that a user cannot modify.
Table 4: Safe-T Policy Parameters


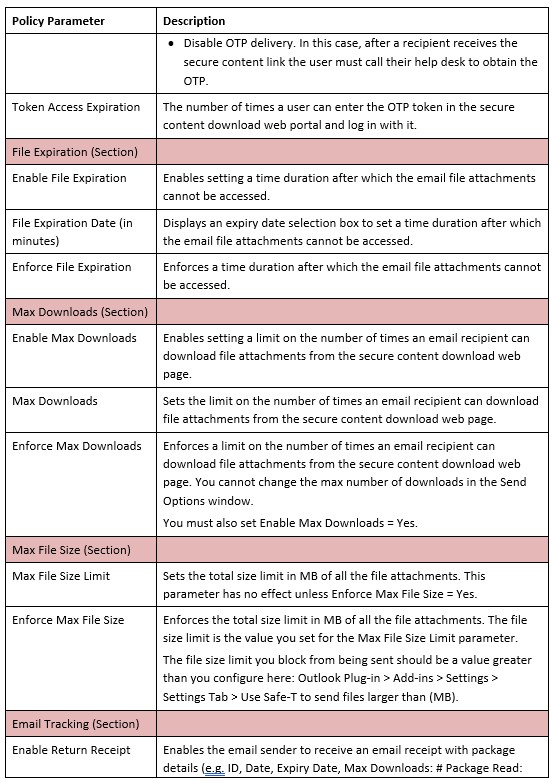


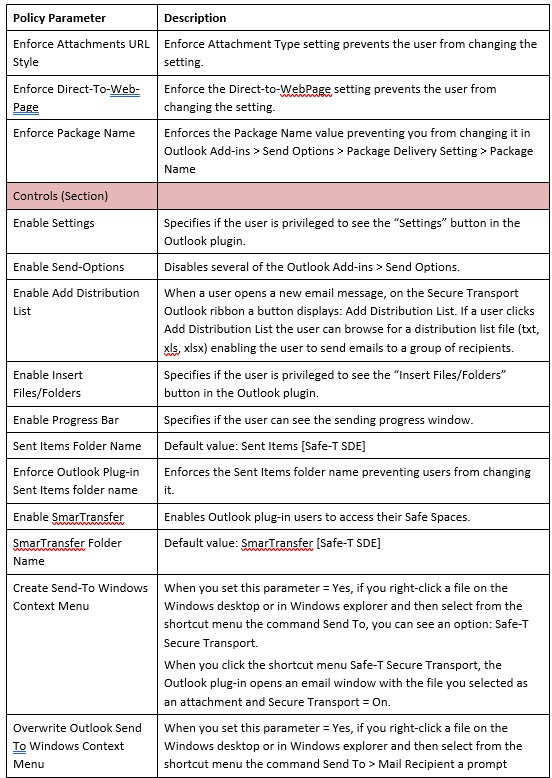


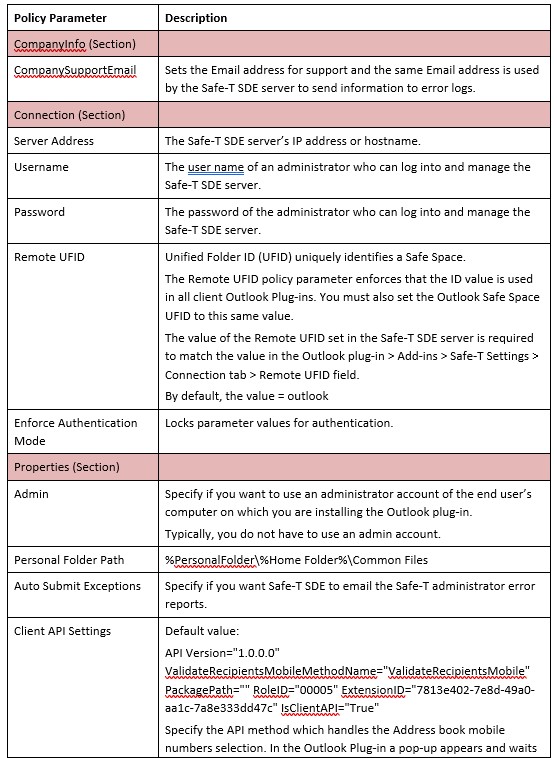
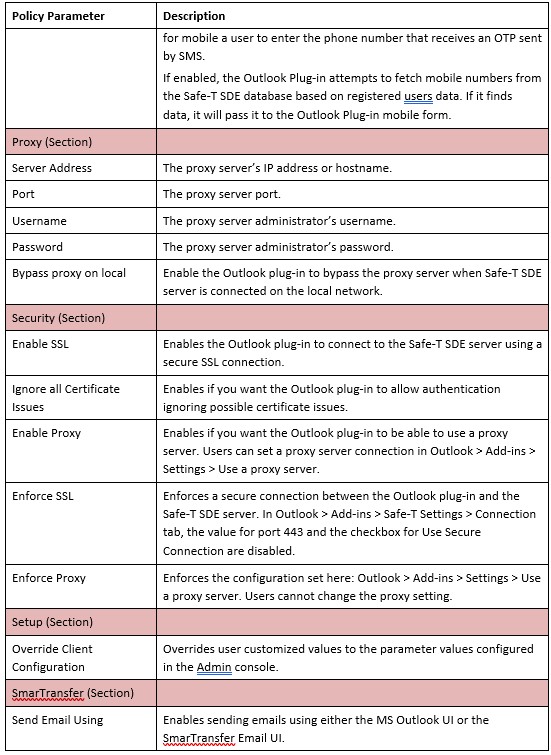
Admin Tasks By Interface
This section provides a table showing the administrative tasks performed by each Safe-T SDE server interface, and several tasks an administrator needs to perform directly on the host Windows server.
Table 5: Admin Clients: Task List

Safe-T Windows Services
This section indicates which Windows Services are used by Safe-T SDE server.
Figure 131: Safe-T SDE Windows Services

Safe-T SDE server uses these Windows services:
• Safe-T SDE Enterprise Service: This is the main Safe-T SDE service.
• Safe-T External Tools Service: The External tools service must have read and write permissions for the local system and remote network files if applicable.
• SQL Server (SQLEXPRESS): The SQL service is related to the default Safe-T SDE server local database.
Tip: You turn off Safe-T SDE services by stopping the Safe-T SDE Enterprise and External Tools Services.
When you click close in the Safe-T SDE Administration console or the Safe-T SDE Configuration tool you close the interface but the Safe-T SDE services continue to run.
Info: Do not stop the Windows SQL Server service which may be shared by other applications on your server. For more information, see How To Stop The Safe-T SDE Server.
Installation Folder Structure
This section describes several essential Safe-T SDE folders. The descriptions are inline and preceded by the # symbol.
Tip: Best Practices: Change the default installation paths given below for the Safe Reply, Safe Spaces, and Outlook archive folder to a non-system drive.
For more information, contact Safe-T Support.
C: \data
This path includes Safe-T job requests: sending emails, file uploads. (Note: File downloads are not jobs, because other than decryption, external tools process files when they are uploaded to a Safe Space.)
-—mailRoot
This folder includes anything that does not use the services of any external tools. If the job succeeds, the files are moved to either the Completed or Badmail subfolders.
\---external.tools
\---queue If any external tools (e.g. encryption, A/V. DLP) are used to process the request the files is queued here: Completed or Badmail folders.
\SafeReply
Default path for any inbound files sent using the safe reply feature.
\SafeSpace
This folder includes your organization’s Safe Spaces. This is a default or example path. Each Safe Space should have its own unique path.
-—MySafespace1 -—MySafespace2 -—MySafespace3 -—Outlook
Default path for Outlook archive Safe Space.
\---Archive\ProgramData\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api|WebSkin
Files that create the web appearance of the end user’s Safe-T web portal.
\Safe-T -—data +---api | -—config | -—Config | -—Schema Files
Schemas: The System schema can be overridden by Safe-T SDE upgrades. The User schema is where your customizations are stored and retained after upgrade.
| \---TemplateHtmlBlocks
| \--- NotificationTemplate_bodyContent.htmlNotificationTemplate_bodyContent.htm: You can modify the background and font of external tools error messages.
| \---RunTime
| \---Apps Path to the compiled connectors folder.
External.Tools.Apps.Apps1 # External.Tools.Apps.Apps2 # External.Tools.Apps.Apps_3 #
Enabling Safe Space Working Folder
This Safe Space working folder feature eliminates possible file use concurrency issues by isolating the process of running a sequence of external tools on one or more files.
Concurrent users are prevented from file upload/download, or online viewing, of the same files until all external tools complete execution.
You can enable this feature in New/Edit Safe Space > Advanced Settings. See Safe Space > Advanced Settings.
Info: The Working Folder feature is enabled by default.
Figure 132: Advanced Settings Working Folder

The Working Folder default path is C:\Temp\Working Folder
If you have not configured any external tools to process file uploads to the Safe Space, the files will not be copied to the Working Folder.
Safe Space Permissions Requirements
- In the New/Edit Safe Space > Connection tab click the Test Connection link and ensure you see a Success message.
- Navigate to the Safe Space folder and verify the Users Group has the Modify permission.
Figure 133: Safe Space Permissions

How The Feature Works
When a user uploads one or more files to a Safe Space, the files are copied to a Working Folder where external tools you previously configured run sequentially (e.g. A/V, DLP). The processed file/s are then copied back to the Safe Space.
If running any of the external tools fails, the resulting action is determined by your configuration in the external tool’s dialog box field: “Delivery”. For example to “Notify on Failure” by sending an administrator an email.
Figure 134: External Tools Resulting Action
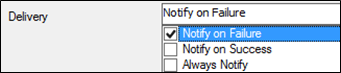
To support using the Safe-T SDE admin web UI, the IIS web portal application pool identity service account must have administrator privileges on the Safe-T SDE server at the same level as the administrator who is responsible for managing the Safe-T SDE External Tools Windows service. The administrator must have modification privileges on all file system folders because the Working Folder can be created using any path the administrator selects.
The default account ApplicationPoolIdentity that exists when you initially create an IIS website does not have sufficient permissions to copy files to and from the Working Folder.
Disabling The Working Folder
The Working Folder feature is active by default and in most uses cases should be enabled. The only reasons an administrator might disable the feature are:
• The Safe Space is used for isolation streaming.
• Troubleshooting.
• A specific requirement in the customer’s IT environment.
Enabling Multi-language Support
Languages supported: English and Hebrew. Default language: English.
Users can switch the display from English to Hebrew in these windows:
• Web Portal login window
• Secure package download window
• Safe-Reply window
The following images show the windows that can be localized.
Figure 135: Safe-T Web Portal Login Window

Figure 136: Secure Package Download Login Window

Note: When a Safe Reply email recipient receives links for secure file download and an invitation to send a Safe Reply, the recipient must select a language in the package download login window.
Figure 137: Safe Reply Window Showing Localization

Enabling Captchas
Captchas can help determine if a user at an authentication window is a human or a machine. This capability mitigates the threat of automated malicious and spam login attempts.
To enable Captchas:
- Log into the Safe-T SDE administrator’s web UI.
- In the navigation pane, select Settings then click the Config link.
- On the Config web page click Captcha.
Figure 138: Captcha Properties

- Enter values for the following fields:
• Use Captcha for OTP: A Captcha appears at the package download window. See, Figure 144 Captcha For OTP.
• Show Captcha immediately: A Captcha appears before each login attempt.
• Show After Num Of Retries: A Captcha does not appear until the user performs the configured number of failed login attempts.
• Use Captcha For Username And Password: A Captcha appears on a username/password authentication window. See, Figure 145 Captcha For Usedrname/Password.
Info: You do not have to activate your configuration changes immediately.
- Restart the Safe-T SDE Enterprise Windows service to activate your configuration changes.
Figure 139: Captcha For OTP
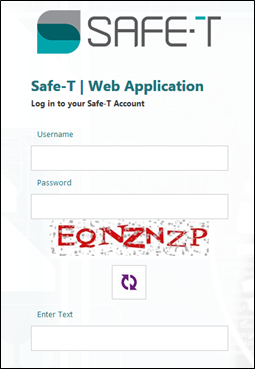
Figure 140: Captcha For Username/Password

Enabling File Attachments Auto Download
The Safe-T auto download capability enables email recipients to access file attachments more efficiently. Auto download is applicable to emails and attachments sent by Secure Transport at level: Normal. By default, the auto download feature is disabled.
Use case: Email recipients click the Secure Content link, then at a package download window enter an OTP or password. Without opening the package download window, the email recipients can save the file attachments to their computers.
Figure 141: Automatically Downloaded File Attachments

Info: The auto download feature is intended for emails sent at secure transport level: Normal. If you enable auto download, emails you send at the High security level send only the file attachments not the encrypted message.
To enable Auto Download:
- In the Safe-T SDE server, navigate to this path:
C:\ProgramData\Safe-T Enterprise\outPost\ui_api
- Open the Web.config file for editing.
- Find the XML key:
<add key="ViewFilePackage_AutoDownload" value="False"/> - Change the value attribute to “True”.
- Save the Web.config file.
- Restart both Windows services:
• Safe-T Box Enterprise Service
• Safe-T Box External Tools Service
Error Message Graphic Format
Figure 142: Example Error Message

You can change the following:
• Background color
• Font type
• Text: This notification was sent to:
Causes of error messages
An external tool can cause an error message to display if a single external tool returns a failure status or if a series of external tools return a failure status. Some, but not all, external tool properties windows contain a Results and a Deliver notification on failure fields.
Figure 143: Example: Deliver Notification on Failure

In the above example, if the McAfee antivirus scan detects an infected file, the system will send a designated administrator a notification message.
Safe-T SDE server sends notification messages to the email address specified in the Email and Text Messaging services > SMTP external tool > Email Address field. See, Extension #17: SMTP Delivery Service.
Figure 144: SMTP Delivery Service: Email Address That Receives System Notifications

To customize the appearance of an external tool error message:
- In the Safe-T SDE file structure, locate this file:
C:\Safe-T\data\api\config\Config\TemplateHtmlBlocks\NotificationTemplate_bodyContent.htm
- Make a backup of the file so you can revert to the default file if you want.
- In an HTML editor, make changes to the file: NotificationTemplate_bodyContent.htm
- Save the file.